Artesunate prevents rats from the clozapine-induced hepatic steatosis and elevation in plasma triglycerides
- PMID: 29026311
- PMCID: PMC5627760
- DOI: 10.2147/NDT.S145069
Artesunate prevents rats from the clozapine-induced hepatic steatosis and elevation in plasma triglycerides
Abstract
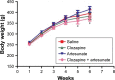
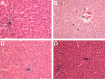
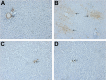
Clozapine is an atypical antipsychotic with therapeutic efficacy in treatment-resistant schizophrenia patients and low incidence of extrapyramidal side effects. However, the use of clozapine has been limited by its adverse effects on metabolism. Artesunate is a semisynthetic derivative of artemisinin and was shown to decrease the plasma cholesterol and triglyceride in rabbits and rats in recent studies. The aim of this study was to examine possible effects of artesunate on the clozapine-induced metabolic alterations in rats given saline, clozapine, artesunate, or clozapine plus artesunate for 6 weeks. The clozapine group showed significantly high plasma levels of triglyceride, hepatic steatosis, and fibrosis along with high levels of C-reactive protein, alanine aminotransferase, and aspartate aminotransferase compared to the saline group. But the treatment had no effect on weight gain and caused no hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, and behavioral changes in the rats. More significantly, these clozapine-induced changes were not seen in rats coadministered with clozapine plus artesunate. These results added evidence supporting psychiatrists to try add-on treatment of artesunate in schizophrenia patients to ameliorate clozapine-induced adverse metabolic effects.
Keywords: artesunate; clozapine; dyslipidemia; hepatic steatosis; schizophrenia.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interests in this work.
Figures



Similar articles
-
cDNA array reveals increased expression of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide following chronic clozapine treatment: role in atypical antipsychotic drug-induced adverse metabolic effects.Pharmacogenomics J. 2006 Mar-Apr;6(2):131-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.tpj.6500346. Pharmacogenomics J. 2006. PMID: 16402076
-
Quetiapine : A Review of its Use in Schizophrenia.CNS Drugs. 1998 Apr;9(4):325-40. doi: 10.2165/00023210-199809040-00007. CNS Drugs. 1998. PMID: 27521016
-
Effects of subchronic clozapine administration on serum glucose, cholesterol and triglyceride levels, and body weight in male BALB/c mice.Life Sci. 2005 Mar 25;76(19):2269-73. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2004.12.004. Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 15733941
-
Metabolic Side Effects from Antipsychotic Treatment with Clozapine Linked to Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) Activation.Biomedicines. 2024 Oct 10;12(10):2294. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12102294. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39457607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Hepatic tolerance of atypical antipsychotic drugs].Encephale. 2002 Nov-Dec;28(6 Pt 1):542-51. Encephale. 2002. PMID: 12506267 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Atypical antipsychotics-induced metabolic syndrome and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a critical review.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019 Jul 22;15:2087-2099. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S208061. eCollection 2019. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2019. PMID: 31413575 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressants- and antipsychotics-induced hepatotoxicity.Arch Toxicol. 2021 Mar;95(3):767-789. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02963-4. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Arch Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33398419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Factors associated with psychological burden of breast cancer in women in Morocco: cross‑sectional study.BMC Womens Health. 2023 Nov 10;23(1):590. doi: 10.1186/s12905-023-02769-3. BMC Womens Health. 2023. PMID: 37950247 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-dependent effects of long-term clozapine or haloperidol medication on red blood cells and liver iron metabolism in Sprague Dawley rats as a model of metabolic syndrome.BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022 Jan 15;23(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s40360-021-00544-4. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35033194 Free PMC article.
-
The Association Between Clozapine Plasma Concentration, CYP2D6 (*10, *2) Polymorphisms and Risk of Adverse Reactions.Psychiatry Clin Psychopharmacol. 2023 Jun 1;33(2):76-83. doi: 10.5152/pcp.2023.22392. eCollection 2023 Jun. Psychiatry Clin Psychopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38765922 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Conley RR, Tamminga CA, Kelly DL, Richardson CM. Treatment-resistant schizophrenic patients respond to clozapine after olanzapine non-response. Biol Psychiatry. 1999;46(1):73–77. - PubMed
-
- Freedman R. Schizophrenia. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:1738–1749. - PubMed
-
- Kane J, Honigfeld G, Singer J, Meltzer H. Clozapine for the treatment-resistant schizophrenic. A double-blind comparison with chlorpromazine. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1988;45(9):789–796. - PubMed
-
- Alvir JM, Lieberman JA. Agranulocytosis: incidence and risk factors. J Clin Psychiatry. 1994;55:137–138. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

