Occurrence of the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) across the Gulf Corporation Council countries: Four years update
- PMID: 29028812
- PMCID: PMC5640221
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0183850
Occurrence of the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) across the Gulf Corporation Council countries: Four years update
Abstract
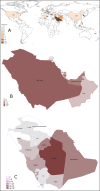
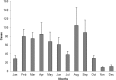
The emergence of the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infections has become a global issue of dire concerns. MERS-CoV infections have been identified in many countries all over the world whereas high level occurrences have been documented in the Middle East and Korea. MERS-CoV is mainly spreading across the geographical region of the Middle East, especially in the Arabian Peninsula, while some imported sporadic cases were reported from the Europe, North America, Africa, and lately Asia. The prevalence of MERS-CoV infections across the Gulf Corporation Council (GCC) countries still remains unclear. Therefore, the objective of the current study was to report the prevalence of MERS-CoV in the GCC countries and to also elucidate on its demographics in the Arabian Peninsula. To date, the World Health Organization (WHO) has reported 1,797 laboratory-confirmed cases of MERS-CoV infection since June 2012, involving 687 deaths in 27 different countries worldwide. Within a time span of 4 years from June 2012 to July 2016, we collect samples form MERS-CoV infected individuals from National Guard Hospital, Riyadh, and Ministry of health Saudi Arabia and other GCC countries. Our data comprise a total of 1550 cases (67.1% male and 32.9% female). The age-specific prevalence and distribution of MERS-CoV was as follow: <20 yrs (36 cases: 3.28%), 20-39 yrs (331 cases: 30.15%), 40-59 yrs (314 cases: 28.60%), and the highest-risk elderly group aged ≥60 yrs (417 cases: 37.98%). The case distribution among GCC countries was as follows: Saudi Arabia (1441 cases: 93%), Kuwait (4 cases: 0.3%), Bahrain (1 case: 0.1%), Oman (8 cases: 0.5%), Qatar (16 cases: 1.0%), and United Arab Emirates (80 cases: 5.2%). Thus, MERS-CoV was found to be more prevalent in Saudi Arabia especially in Riyadh, where 756 cases (52.4%) were the worst hit area of the country identified, followed by the western region Makkah where 298 cases (20.6%) were recorded. This prevalence update indicates that the Arabian Peninsula, particularly Saudi Arabia, is the hardest hit region regarding the emerging MERS-CoV infections worldwide. GCC countries including Saudi Arabia now have the infrastructure in place that allows physicians and scientific community to identify and immediately respond to the potential risks posed by new outbreaks of MERS-CoV infections in the region. Given the continuum of emergence and the large magnitude of the disease in our region, more studies will be required to bolster capabilities for timely detection and effective control and prevention of MERS-CoV in our region.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Public response to MERS-CoV in the Middle East: iPhone survey in six countries.J Infect Public Health. 2017 Sep-Oct;10(5):534-540. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2016.11.015. Epub 2017 Feb 6. J Infect Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28185821 Free PMC article.
-
Global seasonal occurrence of middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018 Jun;22(12):3913-3918. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201806_15276. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29949167
-
Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV): prevention in travelers.Travel Med Infect Dis. 2014 Nov-Dec;12(6 Pt A):602-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tmaid.2014.10.006. Epub 2014 Oct 19. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2014. PMID: 25457301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spatiotemporal Clustering of Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) Incidence in Saudi Arabia, 2012-2019.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Jul 15;16(14):2520. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16142520. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019. PMID: 31311073 Free PMC article.
-
[Etiological, epidemiological and clinical aspects of coronavirus infection MERS-CoV].Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2015 Jan;38(223):46-50. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 2015. PMID: 25763589 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Influenza vaccination situation in Middle-East and North Africa countries: Report of the 7th MENA Influenza Stakeholders Network (MENA-ISN).J Infect Public Health. 2018 Nov-Dec;11(6):845-850. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2018.07.003. Epub 2018 Aug 17. J Infect Public Health. 2018. PMID: 30126699 Free PMC article.
-
Microorganism-ionizing respirator with reduced breathing resistance suitable for removing airborne bacteria.Sens Actuators B Chem. 2018 Dec 10;276:437-446. doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2018.08.133. Epub 2018 Aug 29. Sens Actuators B Chem. 2018. PMID: 32288253 Free PMC article.
-
Narrative review on century of respiratory pandemics from Spanish flu to COVID-19 and impact of nanotechnology on COVID-19 diagnosis and immune system boosting.Virol J. 2022 Oct 24;19(1):167. doi: 10.1186/s12985-022-01902-2. Virol J. 2022. PMID: 36280866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A One Health Perspective on Camel Meat Hygiene and Zoonoses: Insights from a Decade of Research in the Middle East.Vet Sci. 2024 Jul 29;11(8):344. doi: 10.3390/vetsci11080344. Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 39195797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bactrian camels shed large quantities of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) after experimental infection.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2019;8(1):717-723. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2019.1618687. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2019. PMID: 31119984 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zaki AM, van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM, Osterhaus AD, Fouchier RA. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N Engl J Med. 2012;367(19):1814–20. Epub 2012/10/19. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1211721 . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pebody RG, Chand MA, Thomas HL, Green HK, Boddington NL, Carvalho C, et al. The United Kingdom public health response to an imported laboratory confirmed case of a novel coronavirus in September 2012. Euro Surveill. 2012;17(40):20292 Epub 2012/10/20. . - PubMed
-
- van Boheemen S, de Graaf M, Lauber C, Bestebroer TM, Raj VS, Zaki AM, et al. Genomic characterization of a newly discovered coronavirus associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome in humans. MBio. 2012;3(6). Epub 2012/11/22. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00473-12 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3509437. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alagaili AN, Briese T, Mishra N, Kapoor V, Sameroff SC, Burbelo PD, et al. Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection in dromedary camels in Saudi Arabia. MBio. 2014;5(2):e00884–14. Epub 2014/02/27. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00884-14 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3940034. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources