Novel mutations in Darier disease and association to self-reported disease severity
- PMID: 29028823
- PMCID: PMC5640244
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186356
Novel mutations in Darier disease and association to self-reported disease severity
Abstract
Darier disease is a rare and severe autosomal dominant skin disease characterised by malodorous keratotic papules in seborrheic areas of the skin. Darier disease affects up to 1 in 30 000 people and is caused by mutations in the ATP2A2 gene, which encodes to the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum calcium-ATPase isoform 2 that pumps calcium into the endoplasmic reticulum. Although many ATP2A2 variants have been described, it is not known if genotype correlates with phenotype, which could be important for prognosis and treatment. This is the first study to use whole exome sequencing to screen the ATP2A2 gene in a cohort of 28 clinically diagnosed Darier disease patients. Twenty-one different disease causing variants were identified and 15 of these were novel. Sixteen of the 21 variants were predicted to be pathogenic using in silico prediction programs. There were seven missense, four intronic/splice-sites, three frameshifts, two in-frame deletions, four nonsense and one synonymous mutations. This study also found ten patients who harbour more than one ATP2A2 variant. The phenotype of the patient cohort was assessed by photography and by patient questionnaires. The genotype-phenotype association was examined for all variants in relation to the patient's disease severity score, and no correlation could be established.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

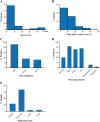

 represent patients who have received laser treatment. The different coloured points represent the patients with two ATP2A2 variants. Points with the same colours are variants in the same patient.
represent patients who have received laser treatment. The different coloured points represent the patients with two ATP2A2 variants. Points with the same colours are variants in the same patient.Similar articles
-
An ATP2A2 Missense Mutation in a Japanese Family with Darier Disease: A Case Report and Review of the Japanese Darier Disease Patients with ATP2A2 Mutations.J Nippon Med Sch. 2017;84(5):246-250. doi: 10.1272/jnms.84.246. J Nippon Med Sch. 2017. PMID: 29142187 Review.
-
Two novel missense mutations of ATP2A2 in two Chinese patients with sporadic Darier disease.Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015 Mar;40(2):201-3. doi: 10.1111/ced.12452. Epub 2014 Oct 4. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25283811
-
Molecular characterization of 11 Italian patients with Darier disease.Eur J Dermatol. 2011 May-Jun;21(3):334-8. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2011.1339. Eur J Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 21527373
-
Darier disease in Slovenia: spectrum of ATP2A2 mutations and relation to patients' phenotypes.Eur J Dermatol. 2010 May-Jun;20(3):271-5. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2010.0913. Epub 2010 Apr 27. Eur J Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 20423818
-
Mendelian Disorders of Cornification Caused by Defects in Intracellular Calcium Pumps: Mutation Update and Database for Variants in ATP2A2 and ATP2C1 Associated with Darier Disease and Hailey-Hailey Disease.Hum Mutat. 2017 Apr;38(4):343-356. doi: 10.1002/humu.23164. Epub 2017 Feb 15. Hum Mutat. 2017. PMID: 28035777 Review.
Cited by
-
Darier disease: first molecular study of a Portuguese family.Heliyon. 2019 Sep 26;5(9):e02520. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02520. eCollection 2019 Sep. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31687605 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a novel nonsense ATP2A2 gene variant in a patient with Darier's disease flare following COVID-19 infection: A case report.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Mar 1;103(9):e37335. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037335. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38428853 Free PMC article.
-
Pumping the Breaks on Acantholytic Skin Disorders: Targeting Calcium Pumps, Desmosomes, and Downstream Signaling in Darier, Hailey-Hailey, and Grover Disease.J Invest Dermatol. 2025 Mar;145(3):494-508. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2024.06.1289. Epub 2024 Aug 29. J Invest Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39207315 Review.
-
Darier disease is associated with heart failure: a cross-sectional case-control and population based study.Sci Rep. 2020 Apr 23;10(1):6886. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63832-9. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32327688 Free PMC article.
-
Severe Darier's Disease by Mitochondrial DNA Insertion Causing Nonsense Mutations: In Silico Prediction of a Pathophysiological Mechanism to a Novel Mutation.Exp Dermatol. 2025 Mar;34(3):e70070. doi: 10.1111/exd.70070. Exp Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40062416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tavadia S, Mortimer E, Munro CS. Genetic epidemiology of Darier’s disease: A population study in the west of Scotland. British Journal of Dermatology. 2002;146:107–109. - PubMed
-
- Burge SM, Wilkinson JD. Darier-White disease: A review of the clinical features in 163 patients. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 1992;27:40–50. - PubMed
-
- Ruiz-Perez VL, Carter SA, Healy E, Todd C, Rees JL, Steijlen PM, et al. ATP2A2 mutations in Darier’s and disease: Variant and cutaneous phenotypes are associated with missense and mutations and but neuropsychiatric features are and independent of mutation class. Human Molecular Genetics. 1999;8:1621–1630. - PubMed
-
- Foggia L, Hovnanian A. Calcium pump disorders of the skin. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part C, Seminars in Medical Genetics. 2004;131C:20–31. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.30031 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Jacobsen NJ, Lyons I, Hoogendoorn B, Burge S, Kwok PY, O’Donovan MC, et al. ATP2A2 mutations in Darier’s disease and their relationship to neuropsychiatric phenotypes. Human Molecular Genetics. 1999;8:1631–1636. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

