Immunogenicity and Safety of an Adjuvanted Herpes Zoster Subunit Vaccine Coadministered With Seasonal Influenza Vaccine in Adults Aged 50 Years or Older
- PMID: 29029224
- PMCID: PMC5853904
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jix481
Immunogenicity and Safety of an Adjuvanted Herpes Zoster Subunit Vaccine Coadministered With Seasonal Influenza Vaccine in Adults Aged 50 Years or Older
Abstract
Background: The immunogenicity and safety of an adjuvanted herpes zoster subunit (HZ/su) vaccine when coadministered with a quadrivalent seasonal inactivated influenza vaccine (IIV4) was investigated in a phase 3, open-label, randomized clinical trial in adults aged ≥50 years.
Methods: Subjects were randomized 1:1 to receive either HZ/su (varicella zoster virus glycoprotein E; AS01B Adjuvant System) and IIV4 at day 0 followed by a second HZ/su dose at month 2 (coadministration group), or IIV4 at month 0 and HZ/su at months 2 and 4 (control group). The primary objectives were the HZ/su vaccine response rate in the coadministration group and the noninferiority of the antibody responses to HZ/su and IIV4 in the coadministration compared with the control group. Safety information was collected throughout the duration of the study.
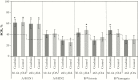
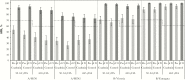
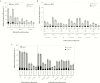
Results: A total of 413 subjects were vaccinated in the coadministration group and 415 in the control group. The HZ/su vaccine response rate in the coadministration group was 95.8% (95% confidence interval, 93.3%-97.6%) and the anti-glycoprotein E GMCControl/Coadmin ratio was 1.08 (.97-1.20). The primary noninferiority objectives were met. No safety concerns were observed.
Conclusions: No interference in the immune responses to either vaccine was observed when the vaccines were coadministered, and no safety concerns were identified.
Clinical trials registration: NCT01954251.
Keywords: adjuvant; coadministration; herpes zoster; influenza; subunit vaccine.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Figures

Comment in
-
Clinical Usage of the Adjuvanted Herpes Zoster Subunit Vaccine (HZ/su): Revaccination of Recipients of Live Attenuated Zoster Vaccine and Coadministration With a Seasonal Influenza Vaccine.J Infect Dis. 2017 Dec 12;216(11):1329-1333. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix484. J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 29029303 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Oxman MN, Levin MJ, Johnson GR et al. ; Shingles Prevention Study Group A vaccine to prevent herpes zoster and postherpetic neuralgia in older adults. N Engl J Med 2005; 352:2271–84. - PubMed
-
- Yawn BP, Saddier P, Wollan PC, St Sauver JL, Kurland MJ, Sy LS. A population-based study of the incidence and complication rates of herpes zoster before zoster vaccine introduction. Mayo Clin Proc 2007; 82:1341–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

