Metabolic characterization and pathway analysis of berberine protects against prostate cancer
- PMID: 29029409
- PMCID: PMC5630309
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.17531
Metabolic characterization and pathway analysis of berberine protects against prostate cancer
Abstract
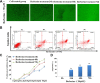
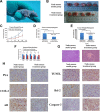
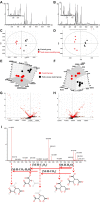
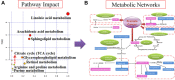
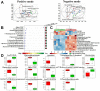
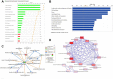
Recent explosion of biological data brings a great challenge for the traditional methods. With increasing scale of large data sets, much advanced tools are required for the depth interpretation problems. As a rapid-developing technology, metabolomics can provide a useful method to discover the pathogenesis of diseases. This study was explored the dynamic changes of metabolic profiling in cells model and Balb/C nude-mouse model of prostate cancer, to clarify the therapeutic mechanism of berberine, as a case study. Here, we report the findings of comprehensive metabolomic investigation of berberine on prostate cancer by high-throughput ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry coupled with pattern recognition methods and network pathway analysis. A total of 30 metabolite biomarkers in blood and 14 metabolites in prostate cancer cell were found from large-scale biological data sets (serum and cell metabolome), respectively. We have constructed a comprehensive metabolic characterization network of berberine to protect against prostate cancer. Furthermore, the results showed that berberine could provide satisfactory effects on prostate cancer via regulating the perturbed pathway. Overall, these findings illustrated the power of the ultra performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry with the pattern recognition analysis for large-scale biological data sets may be promising to yield a valuable tool that insight into the drug action mechanisms and drug discovery as well as help guide testable predictions.
Keywords: UPLC-Q/TOF-MS; metabolome; metabolomics; pathway analysis; prostate cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Zhang A, Zhou X, Zhao H, Zou S, Ma CW, Liu Q, Sun H, Liu L, Wang X. Metabolomics and proteomics technologies to explore the herbal preparation affecting metabolic disorders using high resolution mass spectrometry. Mol Biosyst. 2017;13:320–329. - PubMed
-
- Zhang T, Zhang A, Qiu S, Sun H, Han Y, Guan Y, Wang X. High-throughput metabolomics approach reveals new mechanistic insights for drug response of phenotypes of geniposide towards alcohol-induced liver injury by using liquid chromatography coupled to high resolution mass spectrometry. Mol Biosyst. 2016;13:73–82. - PubMed
-
- Chu H, Zhang A, Han Y, Lu S, Kong L, Han J, Liu Z, Sun H, Wang X. Metabolomics approach to explore the effects of Kai-Xin-San on Alzheimer’s disease using UPLC/ESI-Q-TOF mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016;1015:50–61. - PubMed
-
- Nan Y, Zhou X, Liu Q, Zhang A, Guan Y, Lin S, Kong L, Han Y, Wang X. Serum metabolomics strategy for understanding pharmacological effects of ShenQi pill acting on kidney yang deficiency syndrome. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2016;1026:217–26. - PubMed
-
- Zhang A, Yan G, Zhou X, Wang Y, Han Y, Guan Y, Sun H, Wang X. High resolution metabolomics technology reveals widespread pathway changes of alcoholic liver disease. Mol Biosyst. 2016;12:262–73. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

