B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma: new insights into genetics, molecular aberrations, subclassification and targeted therapy
- PMID: 29029550
- PMCID: PMC5630450
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.19271
B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma: new insights into genetics, molecular aberrations, subclassification and targeted therapy
Abstract
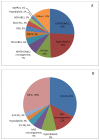
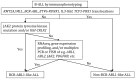
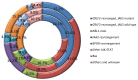
B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (B-ALL) is a clonal hematopoietic stem cell neoplasm derived from B-cell progenitors, which mostly occurs in children and adolescents and is regarded as one of top leading causes of death related to malignancies in this population. Despite the majority of patients with B-ALL have fairly good response to conventional chemotherapeutic interventions followed by hematopoietic stem cell transplant for the last decades, a subpopulation of patients show chemo-resistance and a high relapse rate. Adult B-ALL exhibits similar clinical course but worse prognosis in comparison to younger individuals. Ample evidences have shown that the clinical behavior, response rate and clinical outcome of B-ALL rely largely on its genetic and molecular profiles, such as the presence of BCR-ABL1 fusion gene which is an independent negative prognostic predictor. New B-ALL subtypes have been recognized with recurrent genetic abnormalities, including B-ALL with intrachromosomal amplification of chromosome 21 (iAMP21), B-ALL with translocations involving tyrosine kinases or cytokine receptors ("BCR-ABL1-like ALL"). Genome-wide genetic profiling studies on B-ALL have extended our understanding of genomic landscape of B-ALL, and genetic mutations involved in various key pathways have been illustrated. These include CRLF2 and PAX5 alterations, TP53, CREBBP and ERG mutations, characteristic genetic aberrations in BCR-ABL1-like B-ALL and others. The review further provides new insights into clinical implication of the genetic aberrations in regard to targeted therapy development.
Keywords: B lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma; genetics; molecular biology; predictive markers; prognostic markers.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Swerdlow SH, International Agency for Research on Cancer, World Health Organization . (2008). WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer;
-
- Trigg ME, Sather HN, Reaman GH, Tubergen DG, Steinherz PG, Gaynon PS, Uckun FM, Hammond GD. Ten-year survival of children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Leuk Lymphoma. 2008;49:1142–54. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

