A Case of Aplasia Cutis Congenita Type VI: Bart Syndrome
- PMID: 29033814
- PMCID: PMC5624250
- DOI: 10.1159/000478889
A Case of Aplasia Cutis Congenita Type VI: Bart Syndrome
Abstract
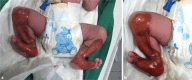
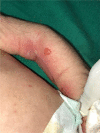
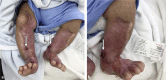
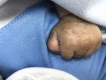
Aplasia cutis congenita type VI, also known as Bart syndrome, is a rare genetic mechanobullous disorder characterized by congenital localized absence of skin, mucocutaneous blistering lesions, and nail abnormalities. We present the case of a 4-h-old male newborn who presented with complete absence of skin over the anteromedial aspect of both lower legs associated with nail dystrophy since birth. After a few days, he developed blisters that were consistent with epidermolysis bullosa in histopathological examination. There was no systemic involvement such as pyloric atresia, ureteral stenosis, renal abnormalities, or arthrogryposis. All laboratory work and imaging studies were normal. A diagnosis of Bart syndrome was made based on previous presentation. We managed the patient with conservative methods. Complete epithelialization occurred after several weeks.
Keywords: Aplasia cutis congenita type VI; Bart syndrome; Conservative treatment; Epidermolysis bullosa.
Figures

References
-
- Bart BJ, Gorlin RJ, Anderson VE, Lynch FW. Congenital localized absence of skin and associated abnormalities resembling epidermolysis bullosa. A new syndrome. Arch Dermatol. 1966;93:296–304. - PubMed
-
- Duran-McKinster C, Rivera-Franco A, Tamayo L, de la Luz Orozco-Covarrubias M, Ruiz-Maldonado R. Bart syndrome: the congenital localized absence of skin may follow the lines of Blaschko. Report of six cases. Pediatr Dermatol. 2000;17:179–182. - PubMed
-
- Frieden IJ. Aplasia cutis congenita: a clinical review and proposal for classification. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1986;14:646–660. - PubMed
-
- Casanova JM, Martí RM, Baradad M, Egido R, Mascaró JM. Bart syndrome associated to lethal junctional epidermolysis bullosa (Herlitz form) (in Spanish). Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2006;97:658–661. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

