Long Non-coding RNAs in Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Cells
- PMID: 29033906
- PMCID: PMC5625025
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01833
Long Non-coding RNAs in Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Cells
Abstract
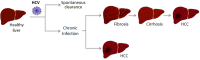
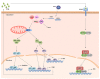
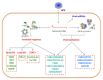
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) often leads to a chronic infection in the liver that may progress to steatosis, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Several viral and cellular factors are required for a productive infection and for the development of liver disease. Some of these are long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) deregulated in infected cells. After HCV infection, the sequence and the structure of the viral RNA genome are sensed to activate interferon (IFN) synthesis and signaling pathways. These antiviral pathways regulate transcription of several cellular lncRNAs. Some of these are also deregulated in response to viral replication. Certain viral proteins and/or viral replication can activate transcription factors such as MYC, SP1, NRF2, or HIF1α that modulate the expression of additional cellular lncRNAs. Interestingly, several lncRNAs deregulated in HCV-infected cells described so far play proviral or antiviral functions by acting as positive or negative regulators of the IFN system, while others help in the development of liver cirrhosis and HCC. The study of the structure and mechanism of action of these lncRNAs may aid in the development of novel strategies to treat infectious and immune pathologies and liver diseases such as cirrhosis and HCC.
Keywords: HCC; HCV; IFN response; antiviral; fibrosis; liver cirrhosis; lncRNAs; proviral.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

