Intraocular pressure monitoring by rebound tonometry in children with myopia
- PMID: 29034154
- PMCID: PMC5637380
- DOI: 10.4103/tjo.tjo_45_17
Intraocular pressure monitoring by rebound tonometry in children with myopia
Abstract
Background/purpose: Topical atropine treatment is generally accepted to retard the progression of myopia, but it is associated with side effects such as photophobia and elevation of intraocular pressure (IOP). IOP measurements in children are challenging. The traditional applanation tonometry by direct contact with the cornea will require patient's cooperation. The rebound tonometer, using a dynamic electromechanical method for measuring IOP, shows good correlation with traditional tonometry. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the IOP of myopic children under atropine treatment using rebound tonometer and to compare the characteristics between rebound tonometry and applanation tonometry.
Methods: This study is a prospective study measuring IOP by rebound tonometer in myopic children under regular low-dose atropine treatment. We recruited children with refraction error showing myopia over -0.5 D with 0.15%, 0.3%, or 0.5% atropine eye drops use every night or every other night for myopia control. Children with treatment duration of atropine <1 month were excluded from the study. IOP measurements were performed by applanation tonometer (Tono-Pen XL, Reichert) and rebound tonometer (ICARE). The reliability of rebound tonometer was analyzed with percentage. Comparison of IOP between rebound tonometer and applanation tonometry was presented.
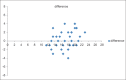
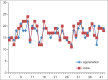
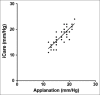
Results: The rebound tonometry was well tolerated by all participants and caused no complaints, discomfort, or adverse events. Totally 42 myopic eyes of 42 subjects were included in the study. The average age of these participants was 10 years old, range from 5 to 16. Median = 10 years old. The average IOP of the right eye by rebound tonometer was 17.4 ± 3 mmHg, and 17.1 ± 3 mmHg by applanation tonometry. Nearly 19%, 33%, and 24% of difference of IOP readings between rebound tonometer and Tono-Pen applanation are within 0 mmHg, 1 mmHg, and 1-2 mmHg, respectively.
Conclusions: Rebound tonometry has good correlation with applanation tonometry and 76.1% of differences between two tonometers are <2 mmHg. The advantage of drop-free rebound tonometry has made it easier to obtain IOP readings in myopia children under atropine treatment.
Keywords: Atropine; intraocular pressure in children; myopia; rebound tonometry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Clinical comparison of the TonoVet(®) rebound tonometer and the Tono-Pen Vet(®) applanation tonometer in dogs and cats with ocular disease: glaucoma or corneal pathology.Vet Ophthalmol. 2015 Jan;18(1):20-7. doi: 10.1111/vop.12101. Epub 2013 Oct 17. Vet Ophthalmol. 2015. PMID: 24131625
-
Accuracy of the new ICare rebound tonometer vs. other portable tonometers in healthy eyes.Optom Vis Sci. 2006 Feb;83(2):102-7. doi: 10.1097/01.opx.0000200673.96758.7b. Optom Vis Sci. 2006. PMID: 16501412
-
Comparison of Intraocular Pressure Measurements between Icare Pro Rebound Tonometer and Tono-Pen XL Tonometer in Supine and Lateral Decubitus Body Positions.Curr Eye Res. 2015 Sep;40(9):923-9. doi: 10.3109/02713683.2014.964416. Epub 2014 Oct 1. Curr Eye Res. 2015. PMID: 25271991
-
Intraocular pressure measurements in paediatric glaucoma: A narrative review on accuracy, tolerability, and ease of use.Med J Malaysia. 2024 Mar;79(2):206-211. Med J Malaysia. 2024. PMID: 38553928 Review.
-
[Contemporary possibilities of intraocular pressure measurement].Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2013 Oct;69(4):175-80. Cesk Slov Oftalmol. 2013. PMID: 24437996 Review. Czech.
Cited by
-
Possibilities of monitoring intraocular pressure in children using EASYTON transpalpebral tonometer.Int Ophthalmol. 2022 May;42(5):1631-1638. doi: 10.1007/s10792-021-02158-5. Epub 2022 Jan 28. Int Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35088357 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of atropine use for myopia control on intraocular pressure in children: A comprehensive review including postpupil dilation intraocular pressure changes.Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2024 Jun 21;14(2):179-189. doi: 10.4103/tjo.TJO-D-24-00026. eCollection 2024 Apr-Jun. Taiwan J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39027062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluating the Effect of Topical Atropine Use for Myopia Control on Intraocular Pressure by Using Machine Learning.J Clin Med. 2020 Dec 30;10(1):111. doi: 10.3390/jcm10010111. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 33396943 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kontiola AI. A new induction-based impact method for measuring intraocular pressure. Acta Ophthalmol Scand. 2000;78:142–5. - PubMed
-
- Wang WH, Millar JC, Pang IH, Wax MB, Clark AF. Noninvasive measurement of rodent intraocular pressure with a rebound tonometer. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46:4617–21. - PubMed
-
- Pakrou N, Gray T, Mills R, Landers J, Craig J. Clinical comparison of the Icare tonometer and Goldmann applanation tonometry. J Glaucoma. 2008;17:43–7. - PubMed
-
- Sahin A, Basmak H, Niyaz L, Yildirim N. Reproducibility and tolerability of the ICare rebound tonometer in school children. J Glaucoma. 2007;16:185–8. - PubMed
-
- Flemmons MS, Hsiao YC, Dzau J, Asrani S, Jones S, Freedman SF. Icare rebound tonometry in children with known and suspected glaucoma. J AAPOS. 2011;15:153–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

