Antidiabetic activity of extracts of Anacardium occidentale Linn. leaves on n-streptozotocin diabetic rats
- PMID: 29034189
- PMCID: PMC5634720
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2016.11.007
Antidiabetic activity of extracts of Anacardium occidentale Linn. leaves on n-streptozotocin diabetic rats
Abstract
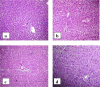
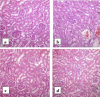
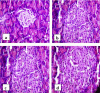
Anacardium occidentale L. (Anacardiaceae) is used in South Cameroon as well as in other tropical countries by traditional practitioners as a folk remedy for treatment of diabetes mellitus. We demonstrated the antidiabetic potential of the plant extracts in n-streptozotocin diabetic rats. The aim of the current study was to investigate the antidiabetic effects of ethanol extract of leaves of A. occidentale on neonatal streptozotocin diabetic rats. Two day old neonates were injected with 100 mg/kg of streptozotocin. At the end of the experimental period of 30 days, reduction in the fasting blood glucose levels, serum insulin, glycated hemoglobin levels, serum lipid parameters, and renal function biomarkers were estimated in the control and treated rats. Histopathological examination of liver, kidney and pancreas were also carried out. On administration of 100 mg/kg of plant extract, blood glucose levels of the rats showed 8.01% and 19.25% decrease in the fasting blood glucose levels on day 15 and day 30, respectively. The administration of extract showed that the effects of extract treatment are comparable to treatment with the standard drug Pioglitazone. These results demonstrate significant antidiabetic potential of the ethanol extract of leaves of A. occidentale, justifying the use of plant in the indigenous system of medicine. Further studies for investigating the specific compound(s) responsible for such beneficial role in diabetes would open new outlook in the therapy of type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Anacardium occidentale; Leaves; Neonatal-induced diabetic rats; Streptozotocin; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Laboratory evaluation of the hypoglycemic effect of Anacardium occidentale Linn (Anacardiaceae) stem-bark extracts in rats.Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2003 Apr;25(3):199-204. doi: 10.1358/mf.2003.25.3.769640. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2003. PMID: 12743624
-
Hypoglycemic effect of methanolic extract of Anacardium occidentale leaves in alloxan-induced diabetic rats.Niger J Physiol Sci. 2010 Nov 25;25(1):87-90. Niger J Physiol Sci. 2010. PMID: 22314909
-
Anacardium occidentale leaves extract and riboceine mitigate hyperglycemia through anti-oxidative effects and modulation of some selected genes associated with diabetes.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022 Dec 8;22(1):455-468. doi: 10.1007/s40200-022-01165-2. eCollection 2023 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2022. PMID: 37255827 Free PMC article.
-
Antihyperglycemic effect of ethanolic extract and fractions of anacardium occidentale L. Stem bark in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.J Basic Clin Pharm. 2009 Dec;1(1):16-9. Epub 2010 Feb 15. J Basic Clin Pharm. 2009. PMID: 25206248 Free PMC article.
-
Acute and subchronic toxicity of Anacardium occidentale Linn (Anacardiaceae) leaves hexane extract in mice.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2006 Nov 13;4(2):140-7. doi: 10.4314/ajtcam.v4i2.31194. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2006. PMID: 20162085 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Antidiabetic Potential of Medicinal Plants and Their Active Components.Biomolecules. 2019 Sep 30;9(10):551. doi: 10.3390/biom9100551. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31575072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antidiabetic Potential of Plants from the Caribbean Basin.Plants (Basel). 2022 May 20;11(10):1360. doi: 10.3390/plants11101360. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antidiabetic effect of Drymaria cordata leaf against streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced diabetic albino rats.J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2020 Jan-Mar;11(1):44-52. doi: 10.4103/japtr.JAPTR_98_19. J Adv Pharm Technol Res. 2020. PMID: 32154158 Free PMC article.
-
Plant-Based Diets and Phytochemicals in the Management of Diabetes Mellitus and Prevention of Its Complications: A Review.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 30;16(21):3709. doi: 10.3390/nu16213709. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39519546 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the antidiabetic potential of compounds isolated from Anacardium occidentale using computational aproach: ligand-based virtual screening.In Silico Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 3;9(1):25. doi: 10.1007/s40203-021-00084-z. eCollection 2021. In Silico Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33868895 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Word Health Organization 2006. http://www.who.org web page: (accessed February, 2012)
-
- Inzucchi S. Classification and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. In: Porte D., Sherwin R., Baron A., editors. Elenberg and Rifkin's Diabetes Mellitus. McGraw Hill; New York: 2003.
-
- Paris R., Plat M., Giono-Barder P., Linhard J., et Laurens A. Recherche chimique et pharmacologique sur les feuilles d’Anacardium occidentale L. (Anacardiace'es) Bull la Société deMédecine d'Afrique Noire Lang Française. 1977;22:275–281. - PubMed
-
- Felcman J., Braganca M.L. Chromium in plants: comparison between the concentration of chromium in Brasilian nonhypo and hypoglycemic plants. Biol Trace Elem Res. 1987;17:11–16. - PubMed
-
- Gupta M., Arias T., Correa M., Lamba S. Ethnopharmacognostic observations on Panamanian medicinal plants. Part I Q J Crude Drug Res. 1979;17:115–130.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
