Cardioprotective effects of Achillea wilhelmsii on the isolated rat heart in ischemia-reperfusion
- PMID: 29034199
- PMCID: PMC5634733
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2016.12.010
Cardioprotective effects of Achillea wilhelmsii on the isolated rat heart in ischemia-reperfusion
Abstract
Context: There are some reports about protective effects of Achillea on the heart.
Objective: We investigated the effect of Achillea wilhelmsii extract on cardiac function during ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury in the isolated rat heart.
Materials and methods: 60 male Wistar rats were randomly divided into 6 groups; 1: Control group, 2: Control-ischemia (CI) 3: vitamin C (10 mg/kg), 4-6: Extract groups (E 100, E 200 and E 400 mg/kg). The animals received normal saline, vitamin C or A. wilhelmsii extract orally for 4 weeks. At the end of the treatment, the hearts were subjected to in vitro I/R Injury (20 min of global ischemia, followed by 40 min of reperfusion, Langendorff's mode). Heart rate (HR) and left ventricular pressure (LVP) were measured using a pressure transducer connected to a data acquisition system. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and creatine kinase (CK) activities in the effluent were measured to determine the myocardial injury degree. The malondialdehyde (MDA), total thiol groups (-SH), superoxide anion dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) in myocardial tissue were detected to determine the oxidative stress degree.
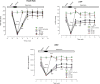
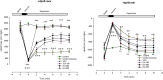
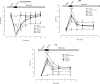
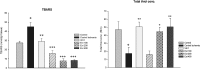
Results: Pretreatment with Achillea wilhlemsii significantly decreased the LDH, CK activities, and MDA level, while it increased the LVDP, ±dp/dtmax, rate-pressure product (RPP), SH groups, SOD and CAT activities, and also the coronary artery flow.
Discussion and conclusion: Our findings indicated that Achillea wilhelmsii could provide protection for heart against the I/R injury which may be related to the improvement of myocardial oxidative stress states.
Keywords: Achillea wilhelmsii; Cardiac function; Ischemia–reperfusion; Oxidative stress; Rat.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Protective Effects of Pharmacologic Postconditioning of Hydroalcoholic Extract of Nigella sativa on Functional Activities and Oxidative Stress Injury During Ischemia-Reperfusion in Isolated Rat Heart.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2020 Apr;20(2):130-138. doi: 10.1007/s12012-019-09540-x. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 31286398
-
Extract from Teucrium polium L. Protects Rat Heart against Oxidative Stress Induced by Ischemic-reperfusion Injury.Adv Biomed Res. 2018 Jan 30;7:15. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_218_16. eCollection 2018. Adv Biomed Res. 2018. PMID: 29456986 Free PMC article.
-
Shenxian-Shengmai Oral Liquid Reduces Myocardial Oxidative Stress and Protects Myocardium from Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(6):2503-2516. doi: 10.1159/000492688. Epub 2018 Aug 17. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30121659
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis of the interventional effects of resveratrol in a rat model of myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jan 19;15:1301502. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1301502. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38313308 Free PMC article.
-
Promising impacts of Achillea spp., beyond A medicinal plant, against toxins, toxicities, and injuries: In vivo and in vitro mechanisms.Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025 Apr 22;42:102023. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2025.102023. eCollection 2025 Jun. Biochem Biophys Rep. 2025. PMID: 40330076 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Green and environmentally friendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles with antibacterial properties from some medicinal plants.BMC Biotechnol. 2024 Jan 23;24(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12896-023-00828-z. BMC Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38263231 Free PMC article.
-
Medicinal Plants in the Treatment of Myocardial Infarction Disease: A Systematic Review.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2024;20(4):e290424229484. doi: 10.2174/011573403X278881240405044328. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2024. PMID: 38685783 Free PMC article.
-
Teucrium polium L. Improved Heart Function and Inhibited Myocardial Apoptosis in Isolated Rat Heart Following Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury.J Pharmacopuncture. 2018 Sep;21(3):159-167. doi: 10.3831/KPI.2018.21.019. Epub 2018 Sep 30. J Pharmacopuncture. 2018. PMID: 30283703 Free PMC article.
-
Salvigenin, a Trimethoxylated Flavone from Achillea Wilhelmsii C. Koch, Exerts Combined Lipid-Lowering and Mitochondrial Stimulatory Effects.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jun 29;10(7):1042. doi: 10.3390/antiox10071042. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34209510 Free PMC article.
-
The Cardioprotective Effects of Aminoguanidine on Lipopolysaccharide Induced Inflammation in Rats.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2020 Oct;20(5):474-481. doi: 10.1007/s12012-020-09570-w. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32232724
References
-
- Fliss H., Gattinger D. Apoptosis in ischemic and reperfused rat myocardium. Circ Res. 1996;79:949–956. - PubMed
-
- Piper H.M., Meuter K., Schafer C. Cellular mechanisms of ischemia-reperfusion injury. Ann Thorac Surg. 2003;75:S644–S648. - PubMed
-
- Jacobson M.D. Reactive oxygen species and programmed cell death. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996;21:83–86. - PubMed
-
- Ryter S.W., Kim H.P., Hoetzel A. Mechanisms of cell death in oxidative stress. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2007;9:49–89. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
