Handshakes and Fights: The Regulatory Interplay of RNA-Binding Proteins
- PMID: 29034245
- PMCID: PMC5626838
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2017.00067
Handshakes and Fights: The Regulatory Interplay of RNA-Binding Proteins
Abstract
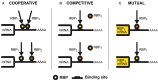
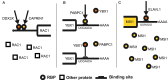
What drives the flow of signals controlling the outcome of post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression? This regulatory layer, presiding to processes ranging from splicing to mRNA stability and localization, is a key determinant of protein levels and thus cell phenotypes. RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) form a remarkable army of post-transcriptional regulators, strong of more than 1,500 genes implementing this expression fine-tuning plan and implicated in both cell physiology and pathology. RBPs can bind and control a wide array of RNA targets. This sheer amount of interactions form complex regulatory networks (PTRNs) where the action of individual RBPs cannot be easily untangled from each other. While past studies have mostly focused on the action of individual RBPs on their targets, we are now observing an increasing amount of evidence describing the occurrence of interactions between RBPs, defining how common target RNAs are regulated. This suggests that the flow of signals in PTRNs is driven by the intertwined contribution of multiple RBPs, concurrently acting on each of their targets. Understanding how RBPs cooperate and compete is thus of paramount importance to chart the wiring of PTRNs and their impact on cell phenotypes. Here we review the current knowledge about patterns of RBP interaction and attempt at describing their general principles. We also discuss future directions which should be taken to reach a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental aspect of gene expression regulation.
Keywords: RNA-binding proteins; autoregulation; competition; cooperation; post-transcriptional regulation; regulatory elements; regulatory networks.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

