Acute Kidney Injury Recognition in Low- and Middle-Income Countries
- PMID: 29034358
- PMCID: PMC5637391
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2017.04.009
Acute Kidney Injury Recognition in Low- and Middle-Income Countries
Abstract
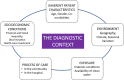
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is increasingly common around the world. Because of the low availability of effective therapies and resource limitations, early preventive and therapeutic measures are essential to decrease morbidity, mortality, and cost. Timely recognition and diagnosis of AKI requires a heightened degree of suspicion in the appropriate clinical and environmental context. In low- and middle-income countries (LMICs), early detection is impaired by limited resources and low awareness. In this article, we report the consensus recommendations of the 18th Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative meeting in Hyderabad, India, on how to improve recognition of AKI. We expect these recommendations will lead to an earlier and more accurate diagnosis of AKI, and improved research to promote a better understanding of the epidemiology, etiology, and histopathology of AKI in LMICs.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; biomarkers; detection; developing countries; diagnosis; recognition; resources.
Figures

References
-
- Mehta R.L., Cerda J., Burdmann E.A. International Society of Nephrology's 0by25 initiative for acute kidney injury (zero preventable deaths by 2025): a human rights case for nephrology. Lancet. 2015;385:2616–2643. - PubMed
-
- Cerda J., Lameire N., Eggers P. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;3:881–886. - PubMed
-
- KDIGO KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline for Acute Kidney Injury. Kidney Int. 2012;Suppl 2:1–138.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
