Treatment history and antimicrobial susceptibility results for Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, and Histophilus somni isolates from bovine respiratory disease cases submitted to the Iowa State University Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory from 2013 to 2015
- PMID: 29034785
- PMCID: PMC6504160
- DOI: 10.1177/1040638717737589
Treatment history and antimicrobial susceptibility results for Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, and Histophilus somni isolates from bovine respiratory disease cases submitted to the Iowa State University Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory from 2013 to 2015
Abstract
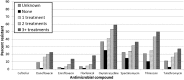
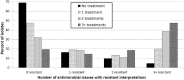
Bovine respiratory disease is the most costly disease facing the cattle industry. Increasing resistance to antimicrobial treatment has been presented as a significant contributing factor, often through summarized susceptibility testing data. We assessed the relationship between previous antimicrobial treatment and antimicrobial susceptibility results from isolates of Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, and Histophilus somni cultured from bovine respiratory cases submitted to the Iowa State University Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory from 2013 to 2015. Antimicrobial susceptibility data from 1,251 bacterial isolates were included for analysis. More bacterial isolates from cattle that received antimicrobial treatment showed resistance compared to isolates from untreated cattle, and the percentage of resistant isolates increased as the number of antimicrobial treatments increased. Resistance to enrofloxacin, spectinomycin, tilmicosin, and tulathromycin was present in >75% of M. haemolytica isolates from cattle that had received 3 or more antimicrobial treatments; resistance to each of those 4 antimicrobials was present in ≤10% of M. haemolytica isolates from untreated cattle. Similar but less dramatic trends were apparent for isolates of P. multocida and H. somni. The percentage of multi-drug resistant bacterial isolates also increased with the number of treatments. Results of our study suggest that previous antimicrobial treatment may have a profound effect on antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Summarized susceptibility results from diagnostic laboratories should not be used to make generalized statements regarding trends in antimicrobial resistance without providing context regarding antimicrobial treatment history.
Keywords: Antimicrobial resistance; Histophilus; Mannheimia; Pasteurella; bovine respiratory disease; susceptibility testing.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prevalence and temporal trends in antimicrobial resistance of bovine respiratory disease pathogen isolates submitted to the Wisconsin Veterinary Diagnostic Laboratory: 2008-2017.J Dairy Sci. 2020 Oct;103(10):9464-9472. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-17570. Epub 2020 Jul 31. J Dairy Sci. 2020. PMID: 32747101
-
A ten-year (2000-2009) study of antimicrobial susceptibility of bacteria that cause bovine respiratory disease complex--Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, and Histophilus somni--in the United States and Canada.J Vet Diagn Invest. 2012 Sep;24(5):932-44. doi: 10.1177/1040638712457559. J Vet Diagn Invest. 2012. PMID: 22914822
-
Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility of Mannheimia haemolytica, Pasteurella multocida, and Histophilus somni isolated from the lower respiratory tract of healthy feedlot cattle and those diagnosed with bovine respiratory disease.Vet Microbiol. 2017 Sep;208:118-125. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2017.07.013. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Vet Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 28888626
-
A literature review of antimicrobial resistance in Pathogens associated with bovine respiratory disease.Anim Health Res Rev. 2015 Dec;16(2):125-34. doi: 10.1017/S146625231500016X. Epub 2015 Sep 16. Anim Health Res Rev. 2015. PMID: 26373635 Review.
-
Bovine pasteurellosis and other bacterial infections of the respiratory tract.Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2010 Mar;26(1):57-71, table of contents. doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2009.10.010. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2010. PMID: 20117542 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between antimicrobial drug class selection for treatment and retreatment of bovine respiratory disease and health, performance, and carcass quality outcomes in feedlot cattle.J Anim Sci. 2020 Apr 1;98(4):skaa109. doi: 10.1093/jas/skaa109. J Anim Sci. 2020. PMID: 32255182 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Antimicrobial Resistance Profile of Respiratory Pathogens Isolated From Suckling Beef Calves to Reprocessing at the Feedlot: A Longitudinal Study.Front Vet Sci. 2021 Nov 2;8:764701. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2021.764701. eCollection 2021. Front Vet Sci. 2021. PMID: 34805342 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial susceptibility and molecular typing of Pasteurella multocida isolated from six provinces in China.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2019 May;51(4):987-992. doi: 10.1007/s11250-018-1754-9. Epub 2018 Dec 10. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2019. PMID: 30535896
-
Characterization and comparison of cell-mediated immune responses following ex vivo stimulation with viral and bacterial respiratory pathogens in stressed and unstressed beef calves1.J Anim Sci. 2019 Jul 2;97(7):2739-2749. doi: 10.1093/jas/skz155. J Anim Sci. 2019. PMID: 31069378 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-Genome Sequence of Multidrug-Resistant Bibersteinia trehalosi Strain OADDL-BT1.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2019 Feb 7;8(6):e01690-18. doi: 10.1128/MRA.01690-18. eCollection 2019 Feb. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2019. PMID: 30746527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance standards for antimicrobial disk dilution susceptibility tests for bacteria isolated from animals; approved standard. 4th ed. Wayne, PA: CLSI, 2013. CLSI document VET01-A4.
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance standards for antimicrobial disk dilution susceptibility tests for bacteria isolated from animals; second informational supplement. Wayne, PA: CLSI, 2013. CLSI document VET01-S2.
-
- DeDonder KD, Apley MD. A literature review of antimicrobial resistance in Pathogens associated with bovine respiratory disease. Anim Health Res Rev 2015;16:125–134. - PubMed
-
- Fales WH, et al. Antimicrobial resistance among Pasteurella spp recovered from Missouri and Iowa cattle with bovine respiratory disease complex. J Am Vet Med Assoc 1982;181:477–479. - PubMed
-
- Griffin D. Economic impact associated with respiratory disease in beef cattle. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract 1997;13:367–377. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

