Lifestyle Medicine: A Brief Review of Its Dramatic Impact on Health and Survival
- PMID: 29035175
- PMCID: PMC5638636
- DOI: 10.7812/TPP/17-025
Lifestyle Medicine: A Brief Review of Its Dramatic Impact on Health and Survival
Abstract
By ignoring the root causes of disease and neglecting to prioritize lifestyle measures for prevention, the medical community is placing people at harm. Advanced nations, influenced by a Western lifestyle, are in the midst of a health crisis, resulting largely from poor lifestyle choices. Epidemiologic, ecologic, and interventional studies have repeatedly indicated that most chronic illnesses, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, and type 2 diabetes, are the result of lifestyles fueled by poor nutrition and physical inactivity.In this article, we describe the practice of lifestyle medicine and its powerful effect on these modern instigators of premature disability and death. We address the economic benefits of prevention-based lifestyle medicine and its effect on our health care system: A system on the verge of bankruptcy. We recommend vital changes to a disastrous course. Many deaths and many causes of pain, suffering, and disability could be circumvented if the medical community could effectively implement and share the power of healthy lifestyle choices. We believe that lifestyle medicine should become the primary approach to the management of chronic conditions and, more importantly, their prevention. For future generations, for our own health, and for the Hippocratic Oath we swore to uphold ("First do no harm"), the medical community must take action. It is our hope that the information presented will inspire our colleagues to pursue lifestyle medicine research and incorporate such practices into their daily care of patients. The time to make this change is now.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
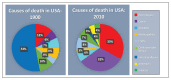
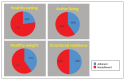
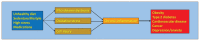
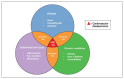
Comment in
-
Lifestyle Medicine in Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Perm J. 2018;22:18-062. doi: 10.7812/TPP/18-062. Perm J. 2018. PMID: 30028672 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Lifestyle Medicine: The Role of the Physical Therapist.Perm J. 2020;24:18.192. doi: 10.7812/TPP/18.192. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Perm J. 2020. PMID: 31905332 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lopez AD, Murray CC. The global burden of disease, 1990–2020. Nat Med. 1990 Nov;4(11):1241–3. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/3218. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Luppino FS, de Wit LM, Bouvy PF, et al. Overweight, obesity, and depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2010 Mar;67(3):220–9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2010.2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nicholson A, Kuper H, Hemmingway H. Depression as an aetiologic and prognostic factor in coronary heart disease: A meta-analysis of 6362 events among 146 538 participants in 54 observational studies. Eur Heart J. 2006 Dec;27(23):2763–74. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehl338. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Hare DL, Toukhsati SR, Johansson P, Jaarsma T. Depression and cardiovascular disease: A clinical review. Eur Heart J. 2014 Jun 1;35(21):1365–72. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/eht462. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tuso P. Treatment progress indicator: Application of a new assessment tool to objectively monitor the therapeutic progress of patients with depression, anxiety, or behavioral impairment. Perm J. 2014 Summer;18(3):55–9. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7812/tpp/13-091. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

