A Wireless Monitoring System Using a Tunneling Sensor Array in a Smart Oral Appliance for Sleep Apnea Treatment
- PMID: 29035296
- PMCID: PMC5677144
- DOI: 10.3390/s17102358
A Wireless Monitoring System Using a Tunneling Sensor Array in a Smart Oral Appliance for Sleep Apnea Treatment
Abstract
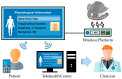
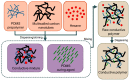
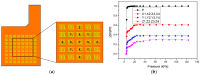
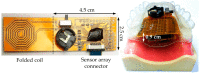
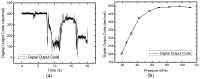
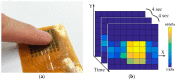
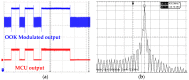
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder, and the most common type is obstructive sleep apnea (OSA). Untreated OSA will cause lots of potential health problems. Oral appliance therapy is an effective and popular approach for OSA treatment, but making a perfect fit for each patient is time-consuming and decreases its efficiency considerably. This paper proposes a System-on-a-Chip (SoC) enabled sleep monitoring system in a smart oral appliance, which is capable of intelligently collecting the physiological data about tongue movement through the whole therapy. A tunneling sensor array with an ultra-high sensitivity is incorporated to accurately detect the subtle pressure from the tongue. When the device is placed on the wireless platform, the temporary stored data will be retrieved and wirelessly transmitted to personal computers and cloud storages. The battery will be recharged by harvesting external RF power from the platform. A compact prototype module, whose size is 4.5 × 2.5 × 0.9 cm³, is implemented and embedded inside the oral appliance to demonstrate the tongue movement detection in continuous time frames. The functions of this design are verified by the presented measurement results. This design aims to increase efficiency and make it a total solution for OSA treatment.
Keywords: OSA; SoC; prototype module; sleep apnea; sleep monitoring; smart oral appliance; tunneling sensor; wireless.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Comparison of a simple obstructive sleep apnea screening device with standard in-laboratory polysomnography.Sleep Breath. 2016 May;20(2):537-41. doi: 10.1007/s11325-015-1234-7. Epub 2015 Aug 12. Sleep Breath. 2016. PMID: 26265559
-
The difference between two oral appliances in treating obstructive sleep apnea: a case report.J Formos Med Assoc. 2010 Feb;109(2):163-6. doi: 10.1016/S0929-6646(10)60037-X. J Formos Med Assoc. 2010. PMID: 20206841
-
Selection of response criteria affects the success rate of oral appliance treatment for obstructive sleep apnea.Sleep Med. 2014 Mar;15(3):367-70. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2013.12.007. Epub 2014 Jan 27. Sleep Med. 2014. PMID: 24560190
-
Management of obstructive sleep apnea in edentulous patients: an overview of the literature.Sleep Breath. 2016 Mar;20(1):395-404. doi: 10.1007/s11325-015-1285-9. Epub 2015 Nov 19. Sleep Breath. 2016. PMID: 26585170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contemporary issues in the diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea.Postgrad Med. 2008 Jul;120(2):46-52. doi: 10.3810/pgm.2008.07.1790. Postgrad Med. 2008. PMID: 18654068 Review.
Cited by
-
Precision medicine approaches in obstructive sleep apnoea: The role of dentist-sleep physician partnerships.Aust Dent J. 2024 Jun;69 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S21-S30. doi: 10.1111/adj.13039. Epub 2024 Oct 1. Aust Dent J. 2024. PMID: 39354705 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Biomechanical Mechanism of Upper Airway Collapse in OSAHS Patients Using Clinical Monitoring Data during Natural Sleep.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Nov 10;21(22):7457. doi: 10.3390/s21227457. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34833533 Free PMC article.
-
Smart mandibular advancement devices for obstructive sleep apnea: a systematic literature review.Sleep Breath. 2024 Oct;28(5):1879-1887. doi: 10.1007/s11325-024-03068-3. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Sleep Breath. 2024. PMID: 38886278 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Institutes of Health National Institutes of Health Sleep Disorders Research Plan. [(accessed on 1 October 2011)];2011 Nov; Available online: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-pro/resources/sleep/nih-sleep-disorders....
-
- Standards of Practice Committee of the American Sleep Disorders Association Practice parameters for the indications for polysomnography and related procedures. Sleep. 1997;20:406–422. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

