Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 and Oligodendrogenesis: Significance in Alcohol Use Disorders
- PMID: 29035306
- PMCID: PMC5664058
- DOI: 10.3390/brainsci7100131
Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 and Oligodendrogenesis: Significance in Alcohol Use Disorders
Abstract
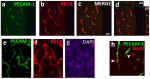
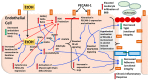
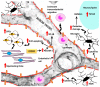
Alcoholism is a chronic relapsing disorder with few therapeutic strategies that address the core pathophysiology. Brain tissue loss and oxidative damage are key components of alcoholism, such that reversal of these phenomena may help break the addictive cycle in alcohol use disorder (AUD). The current review focuses on platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule 1 (PECAM-1), a key modulator of the cerebral endothelial integrity and neuroinflammation, and a targetable transmembrane protein whose interaction within AUD has not been well explored. The current review will elaborate on the function of PECAM-1 in physiology and pathology and infer its contribution in AUD neuropathology. Recent research reveals that oligodendrocytes, whose primary function is myelination of neurons in the brain, are a key component in new learning and adaptation to environmental challenges. The current review briefly introduces the role of oligodendrocytes in healthy physiology and neuropathology. Importantly, we will highlight the recent evidence of dysregulation of oligodendrocytes in the context of AUD and then discuss their potential interaction with PECAM-1 on the cerebral endothelium.
Keywords: PECAM-1; alcohol; blood–brain barrier; endothelium; myelin; oligodendroglia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

