Targeting glioma stem cells through combined BMI1 and EZH2 inhibition
- PMID: 29035367
- PMCID: PMC5679732
- DOI: 10.1038/nm.4415
Targeting glioma stem cells through combined BMI1 and EZH2 inhibition
Abstract
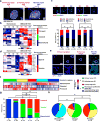
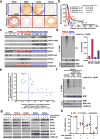
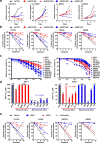
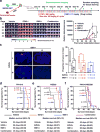
Glioblastomas are lethal cancers defined by angiogenesis and pseudopalisading necrosis. Here, we demonstrate that these histological features are associated with distinct transcriptional programs, with vascular regions showing a proneural profile, and hypoxic regions showing a mesenchymal pattern. As these regions harbor glioma stem cells (GSCs), we investigated the epigenetic regulation of these two niches. Proneural, perivascular GSCs activated EZH2, whereas mesenchymal GSCs in hypoxic regions expressed BMI1 protein, which promoted cellular survival under stress due to downregulation of the E3 ligase RNF144A. Using both genetic and pharmacologic inhibition, we found that proneural GSCs are preferentially sensitive to EZH2 disruption, whereas mesenchymal GSCs are more sensitive to BMI1 inhibition. Given that glioblastomas contain both proneural and mesenchymal GSCs, combined EZH2 and BMI1 targeting proved more effective than either agent alone both in culture and in vivo, suggesting that strategies that simultaneously target multiple epigenetic regulators within glioblastomas may be effective in overcoming therapy resistance caused by intratumoral heterogeneity.
Conflict of interest statement
JNR received an honorarium from PTC Therapeutics as an advisory board member. No other author declares competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Wen PY, Kesari S. Malignant Gliomas in Adults. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:492–507. - PubMed
-
- Singh SK, et al. Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature. 2004;432:396–401. - PubMed
-
- Galli R, et al. Isolation and Characterization of Tumorigenic, Stem-like Neural Precursors from Human Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7011–7021. - PubMed
-
- Jin X, et al. Blockade of EGFR signaling promotes glioma stem-like cell invasiveness by abolishing ID3-mediated inhibition of p27KIP1 and MMP3 expression. Cancer Lett. 2013;328:235–242. - PubMed
-
- Bao S, et al. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature. 2006;444:756–760. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 CA169117/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 CA217065/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS099175/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 CA217066/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS087913/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS103434/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197718/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 CA183510/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 CA203101/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS091080/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA184090/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA171652/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS089272/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007250/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA154130/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

