Design and characterization of MP0250, a tri-specific anti-HGF/anti-VEGF DARPin® drug candidate
- PMID: 29035637
- PMCID: PMC5680794
- DOI: 10.1080/19420862.2017.1305529
Design and characterization of MP0250, a tri-specific anti-HGF/anti-VEGF DARPin® drug candidate
Abstract
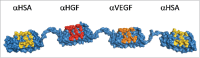
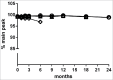
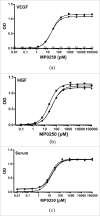
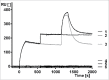
MP0250 is a multi-domain drug candidate currently being tested in clinical trials for the treatment of cancer. It comprises one anti-vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF-A), one anti-hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), and two anti-human serum albumin (HSA) DARPin® domains within a single polypeptide chain. While there is first clinical validation of a single-domain DARPin® drug candidate, little is known about DARPin® drug candidates comprising multiple domains. Here, we show that MP0250 can be expressed at 15 g/L in soluble form in E. coli high cell-density fermentation, it is stable in soluble/frozen formulation for 2 years as assessed by reverse phase HPLC, it has picomolar potency in inhibiting VEGF-A and HGF in ELISA and cellular assays, and its domains are simultaneously active as shown by surface plasmon resonance. The inclusion of HSA-binding DARPin® domains leads to a favorable pharmacokinetic profile in mouse and cynomolgus monkey, with terminal half-lives of ∼ 30 hours in mouse and ∼ 5 days in cynomolgus monkey. MP0250 is thus a highly potent drug candidate that could be particularly useful in oncology. Beyond MP0250, the properties of MP0250 indicate that multi-domain DARPin® proteins can be valuable next-generation drug candidates.
Keywords: DARPin®; HGF; VEGF; multi-specificity; pharmacokinetics; serum albumin.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
