Identification of N-linked glycosylation sites in the spike protein and their functional impact on the replication and infectivity of coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus in cell culture
- PMID: 29035787
- PMCID: PMC7112133
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virol.2017.10.003
Identification of N-linked glycosylation sites in the spike protein and their functional impact on the replication and infectivity of coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus in cell culture
Abstract
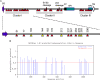
Spike (S) glycoprotein on the viral envelope is the main determinant of infectivity. The S protein of coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus (IBV) contains 29 putative asparagine(N)-linked glycosylation sites. These post-translational modifications may assist in protein folding and play important roles in the functionality of S protein. In this study, we used bioinformatics tools to predict N-linked glycosylation sites and to analyze their distribution in IBV strains and variants. Among these sites, 8 sites were confirmed in the S protein extracted from partially purified virus particles by proteomics approaches. N-D and N-Q substitutions at 13 predicted sites were introduced into an infectious clone system. The impact on S protein-mediated cell-cell fusion, viral recovery and infectivity was assessed, leading to the identification of sites essential for the functions of IBV S protein. Further characterization of these and other uncharacterized sites may reveal novel aspects of N-linked glycosylation in coronavirus replication and pathogenesis.
Keywords: Cell-cell fusion; Clone; Coronavirus; Infectious bronchitis virus; Infectious cDNA; N-linked glycosylation; Spike protein; Virus infectivity.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



References
-
- Arjona A., Ledizet M., Anthony K., Bonafé N., Modis Y., Town T., Fikrig E. West Nile virus envelope protein inhibits dsRNA-induced innate immune responses. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md. 2007;1950(179):8403–8409. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

