MRI-assessed atrophy subtypes in Alzheimer's disease and the cognitive reserve hypothesis
- PMID: 29036183
- PMCID: PMC5643102
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0186595
MRI-assessed atrophy subtypes in Alzheimer's disease and the cognitive reserve hypothesis
Abstract
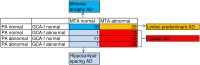
Background/aims: MRI assessment of the brain has demonstrated four different patterns of atrophy in patients with Alzheimer's disease dementia (AD): typical AD, limbic-predominant AD, hippocampal-sparing AD, and a subtype with minimal atrophy, previously referred to as no-atrophy AD. The aim of the present study was to identify and describe the differences between these four AD subtypes in a longitudinal memory-clinic study.
Methods: The medial temporal lobes, the frontal regions, and the posterior regions were assessed with MRI visual rating scales to categorize 123 patients with mild AD according to ICD-10 and NINCDS-ADRDA criteria and the clinical dementia rating scale (CDR) into atrophy subtypes. Demographic data, neuropsychological measures, cerebrospinal-fluid biomarkers, and progression rate of dementia at two-year follow-up were compared between the groups.
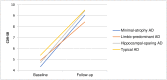
Results: Typical AD was found in 59 patients (48%); 29 (24%) patients had limbic-predominant AD; 19 (15%) had hippocampal-sparing AD; and 16 (13%) belonged to the group with minimal atrophy. No differences were found regarding cognitive test results or progression rates between the different subtypes. Using adjusted logistic regression analysis, we found that the patients in the minimal-atrophy group were less educated, had a lower baseline CDR sum of boxes score, and had higher levels of amyloid β in the cerebrospinal fluid.
Conclusion: Previous results concerning the prevalence and the similar phenotypic expressions of the four AD subtypes were confirmed. The main finding was that patients with minimal atrophy as assessed by MRI had less education than the other AD subtypes and that this could support the cognitive reserve hypothesis and, at least in part, explain the lower degree of atrophy in this group. Patients with less formal education might present with clinically typical AD symptoms before they have positive biomarkers of AD and this finding might challenge suggested biomarker-based criteria for AD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman BT, Jack CR Jr, Kawas CH, et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease: Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7:263–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Koedam EL, Lauffer V, van der Vlies AE, van der Flier WM, Scheltens P, Pijnenburg YA. Early-versus late-onset Alzheimer's disease: more than age alone. J Alzheimers Dis. 2010;19:1401–8. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-1337 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Holtzman DM, Morris JC, Goate AM. Alzheimer's disease: the challenge of the second century. Sci Transl Med. 2011;3:77sr1 doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002369 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Braak E. Evolution of the neuropathology of Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1996;165:3–12. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical