Radiomic subtyping improves disease stratification beyond key molecular, clinical, and standard imaging characteristics in patients with glioblastoma
- PMID: 29036412
- PMCID: PMC5961168
- DOI: 10.1093/neuonc/nox188
Radiomic subtyping improves disease stratification beyond key molecular, clinical, and standard imaging characteristics in patients with glioblastoma
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to analyze the potential of radiomics for disease stratification beyond key molecular, clinical, and standard imaging features in patients with glioblastoma.
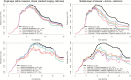
Methods: Quantitative imaging features (n = 1043) were extracted from the multiparametric MRI of 181 patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma prior to standard-of-care treatment (allocated to a discovery and a validation set, 2:1 ratio). A subset of 386/1043 features were identified as reproducible (in an independent MRI test-retest cohort) and selected for analysis. A penalized Cox model with 10-fold cross-validation (Coxnet) was fitted on the discovery set to construct a radiomic signature for predicting progression-free and overall survival (PFS and OS). The incremental value of a radiomic signature beyond molecular (O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase [MGMT] promoter methylation, DNA methylation subgroups), clinical (patient's age, KPS, extent of resection, adjuvant treatment), and standard imaging parameters (tumor volumes) for stratifying PFS and OS was assessed with multivariate Cox models (performance quantified with prediction error curves).
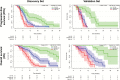
Results: The radiomic signature (constructed from 8/386 features identified through Coxnet) increased the prediction accuracy for PFS and OS (in both discovery and validation sets) beyond the assessed molecular, clinical, and standard imaging parameters (P ≤ 0.01). Prediction errors decreased by 36% for PFS and 37% for OS when adding the radiomic signature (compared with 29% and 27%, respectively, with molecular + clinical features alone). The radiomic signature was-along with MGMT status-the only parameter with independent significance on multivariate analysis (P ≤ 0.01).
Conclusions: Our study stresses the role of integrating radiomics into a multilayer decision framework with key molecular and clinical features to improve disease stratification and to potentially advance personalized treatment of patients with glioblastoma.
Figures


References
-
- Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, et al. ; European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumor and Radiotherapy Groups; National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):987–996. - PubMed
-
- Wick W, Weller M, van den Bent M, et al. . MGMT testing–the challenges for biomarker-based glioma treatment. Nat Rev Neurol. 2014;10(7):372–385. - PubMed
-
- Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, et al. . MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):997–1003. - PubMed
-
- Wick W, Platten M, Meisner C, et al. ; NOA-08 Study Group of Neuro-oncology Working Group (NOA) of German Cancer Society Temozolomide chemotherapy alone versus radiotherapy alone for malignant astrocytoma in the elderly: the NOA-08 randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(7):707–715. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

