2'-Fluoroarabinonucleic acid modification traps G-quadruplex and i-motif structures in human telomeric DNA
- PMID: 29036537
- PMCID: PMC5714228
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx838
2'-Fluoroarabinonucleic acid modification traps G-quadruplex and i-motif structures in human telomeric DNA
Erratum in
-
2'-Fluoroarabinonucleic acid modification traps G-quadruplex and i-motif structures in human telomeric DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 16;45(20):12055. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx962. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 29040679 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
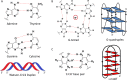
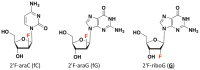
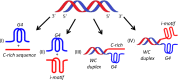
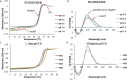
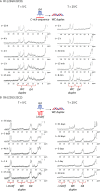
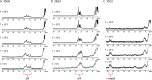
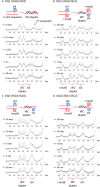
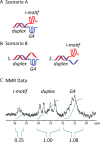
Human telomeres and promoter regions of genes fulfill a significant role in cellular aging and cancer. These regions comprise of guanine and cytosine-rich repeats, which under certain conditions can fold into G-quadruplex (G4) and i-motif structures, respectively. Herein, we use UV, circular dichroism and NMR spectroscopy to study several human telomeric sequences and demonstrate that G4/i-motif-duplex interconversion kinetics are slowed down dramatically by 2'-β-fluorination and the presence of G4/i-motif-duplex junctions. NMR-monitored kinetic experiments on 1:1 mixtures of native and modified C- and G-rich human telomeric sequences reveal that strand hybridization kinetics are controlled by G4 or i-motif unfolding. Furthermore, we provide NMR evidence for the formation of a hybrid complex containing G4 and i-motif structures proximal to a duplex DNA segment at neutral pH. While the presence of i-motif and G4 folds may be mutually exclusive in promoter genome sequences, our results suggest that they may co-exist transiently as intermediates in telomeric sequences.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Blackburn E.H., Epel E.S., Lin J.. Human telomere biology: a contributory and interactive factor in aging, disease risks, and protection. Science. 2015; 350:1193–1198. - PubMed
-
- Sen D., Gilbert W.. Formation of parallel 4-stranded complexes by guanine-rich motifs in DNA and its implications for meiosis. Nature. 1988; 334:364–366. - PubMed
-
- Williamson J.R., Raghuraman M.K., Cech T.R.. Mono-valent cation induced structure of telomeric DNA—the G-Quartet model. Cell. 1989; 59:871–880. - PubMed
-
- Lipps H.J., Rhodes D.. G-quadruplex structures: in vivo evidence and function. Trends Cell Biol. 2009; 19:414–422. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

