Database Resources of the BIG Data Center in 2018
- PMID: 29036542
- PMCID: PMC5753194
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx897
Database Resources of the BIG Data Center in 2018
Abstract
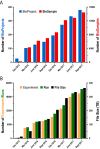
The BIG Data Center at Beijing Institute of Genomics (BIG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences provides freely open access to a suite of database resources in support of worldwide research activities in both academia and industry. With the vast amounts of omics data generated at ever-greater scales and rates, the BIG Data Center is continually expanding, updating and enriching its core database resources through big-data integration and value-added curation, including BioCode (a repository archiving bioinformatics tool codes), BioProject (a biological project library), BioSample (a biological sample library), Genome Sequence Archive (GSA, a data repository for archiving raw sequence reads), Genome Warehouse (GWH, a centralized resource housing genome-scale data), Genome Variation Map (GVM, a public repository of genome variations), Gene Expression Nebulas (GEN, a database of gene expression profiles based on RNA-Seq data), Methylation Bank (MethBank, an integrated databank of DNA methylomes), and Science Wikis (a series of biological knowledge wikis for community annotations). In addition, three featured web services are provided, viz., BIG Search (search as a service; a scalable inter-domain text search engine), BIG SSO (single sign-on as a service; a user access control system to gain access to multiple independent systems with a single ID and password) and Gsub (submission as a service; a unified submission service for all relevant resources). All of these resources are publicly accessible through the home page of the BIG Data Center at http://bigd.big.ac.cn.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Cyranoski D. China embraces precision medicine on a massive scale. Nature. 2016; 529:9–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

