Impacts of Electroconvulsive Therapy on 1-Year Outcomes in Patients With Schizophrenia: A Controlled, Population-Based Mirror-Image Study
- PMID: 29036711
- PMCID: PMC6007329
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbx136
Impacts of Electroconvulsive Therapy on 1-Year Outcomes in Patients With Schizophrenia: A Controlled, Population-Based Mirror-Image Study
Abstract
Objectives: Despite the decline in the use of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) in patients with schizophrenia, ECT augmentation is still recommended for those with poor response to standard pharmacological intervention. However, the effectiveness of augmentation of antipsychotics with ECT on long-term clinical outcomes needs to be verified in an expanded sample.
Methods: Patients who were hospitalized for schizophrenia and received ECT for the first time during that hospitalization were identified from the total population health insurance database in Taiwan between 2002 and 2011. A comparison group was randomly selected and matched by age, gender, calendar year of hospitalization, and duration of hospitalization. Using a mirror-image design, the changes in rates of psychiatric and overall hospitalization, length of hospital stay, number of emergency department visits, and direct medical costs across the 1-year pre- and post-treatment periods were examined.
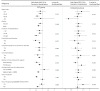
Results: A total of 2074 patients with the same number of comparison participants were included in the analysis. The rate of re-hospitalization decreased significantly in the ECT group during the 1-year post-treatment period, while there was no significant difference in the comparison group. Correspondingly, the total medical expenses increased significantly in the non-ECT group, but not in the ECT group. Notably, the reduction in the psychiatric re-hospitalization rate in the ECT group was more pronounced among those treated with clozapine or a medium-high average daily dose of antipsychotics.
Conclusion: This 1-year mirror-image analysis indicated that augmentation of antipsychotics with ECT in schizophrenic patients was associated with a reduced rate of psychiatric re-hospitalization.
Figures

References
-
- Whiteford HA, Degenhardt L, Rehm J, et al. Global burden of disease attributable to mental and substance use disorders: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. The Lancet 2013;382:1575–1586. - PubMed
-
- Brenner HD, Dencker SJ, Goldstein MJ, et al. Defining treatment refractoriness in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 1990;16:551–561. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy JL, Altar CA, Taylor DL, Degtiar I, Hornberger JC. The social and economic burden of treatment-resistant schizophrenia: a systematic literature review. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2014;29:63–76. - PubMed
-
- Endler NS. The origins of electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). Convuls Ther. 1988;4:5–23. - PubMed
-
- Tharyan P, Adams CE. Electroconvulsive therapy for schizophrenia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005:CD000076. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

