A vicious circle between insulin resistance and inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 29037210
- PMCID: PMC5644081
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-017-0572-9
A vicious circle between insulin resistance and inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Erratum in
-
Correction to: A vicious circle between insulin resistance and inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Feb 23;17(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0678-8. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 29475442 Free PMC article.
Abstract
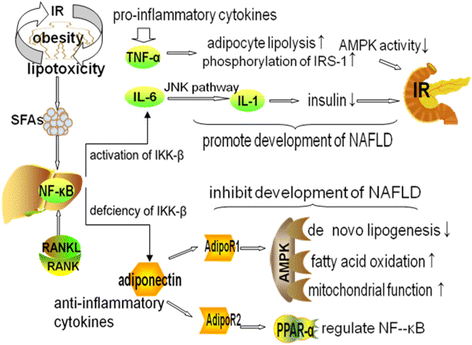
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) comprises a spectrum of diseases, including simple steatosis, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Lipotoxicity, insulin resistance (IR) and inflammation are involved in the disease process. Lipotoxicity promotes inflammation and IR, which in turn, increase adipocyte lipolysis and exacerbates lipotoxicity. Furthermore, IR and inflammation form a vicious circle, with each condition promoting the other and accelerating the development of NAFLD in the presence of lipotoxicity. As an integrator of inflammatory pathway networks, nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) regulates expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin 6 (IL-6), and anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as adiponectin in NAFLD. In this review, the relationships between lipotoxicity, IR and inflammation in NAFLD are discussed, with particular emphasis on the inflammatory pathways.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Yes.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Wong RJ, Aguilar M, Cheung R, Perumpail RB, Harrison SA, Younossi ZM, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2015;148(3):547–555. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.11.039. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

