A novel protein derived from lamprey supraneural body tissue with efficient cytocidal actions against tumor cells
- PMID: 29037260
- PMCID: PMC5644163
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-017-0198-6
A novel protein derived from lamprey supraneural body tissue with efficient cytocidal actions against tumor cells
Erratum in
-
Correction to: A novel protein derived from lamprey supraneural body tissue with efficient cytocidal actions against tumor cells.Cell Commun Signal. 2017 Nov 27;15(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12964-017-0202-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2017. PMID: 29179762 Free PMC article.
Abstract
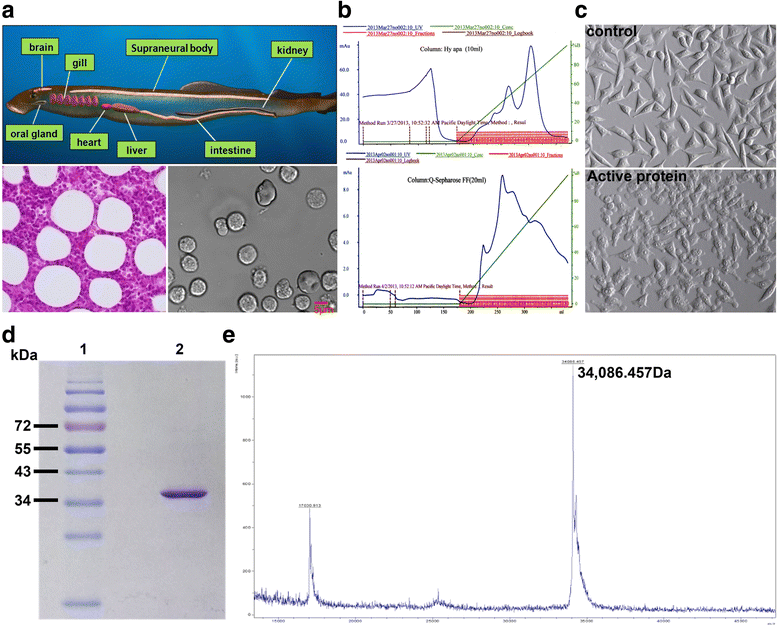
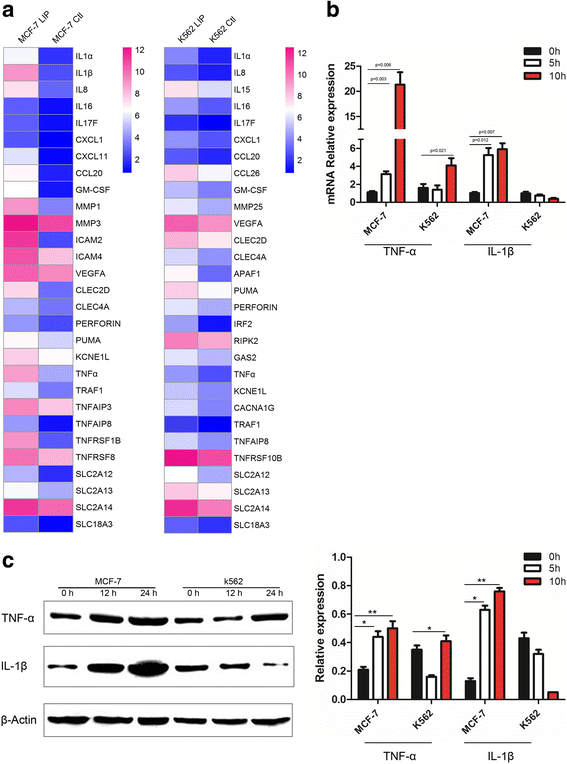
Background: In previous research, we found that cell secretion from the adult lamprey supraneural body tissues possesses cytocidal activity against tumor cells, but the protein with cytocidal activity was unidentified.
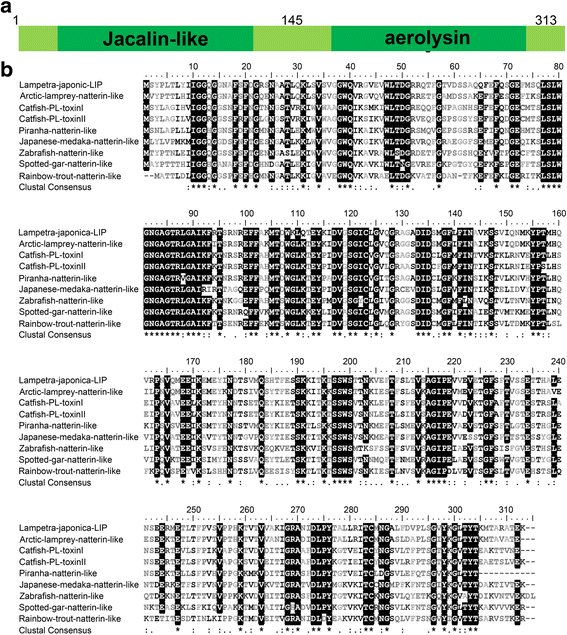
Methods: A novel lamprey immune protein (LIP) as defense molecule was first purified and identified in jawless vertebrates (cyclostomes) using hydroxyapatite column and Q Sepharose Fast Flow column. After LIP stimulation, morphological changes of tumor cells were analysed and measured whether in vivo or in vitro.
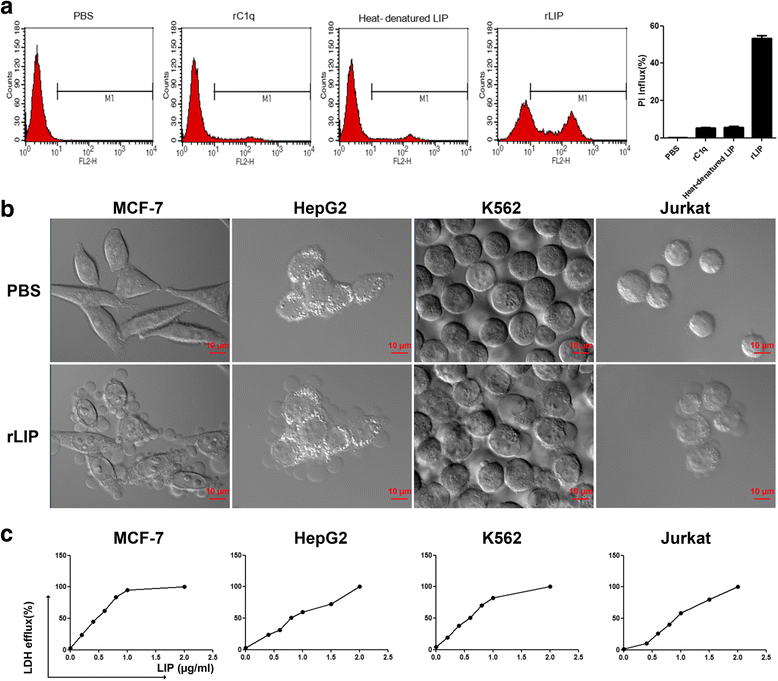
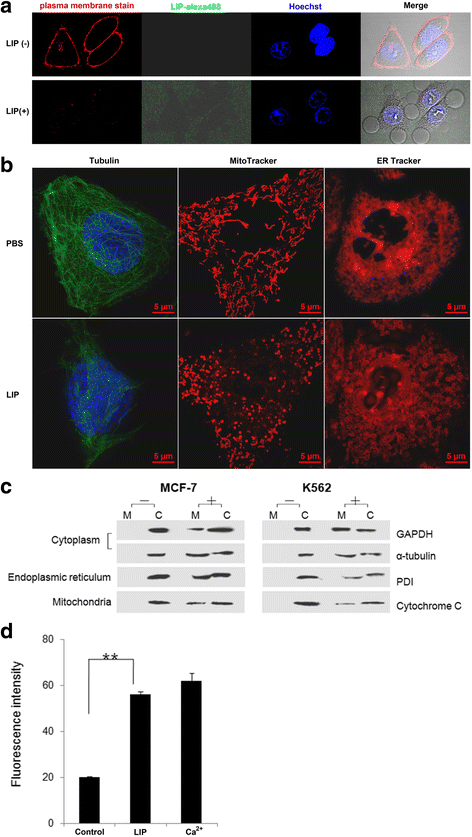
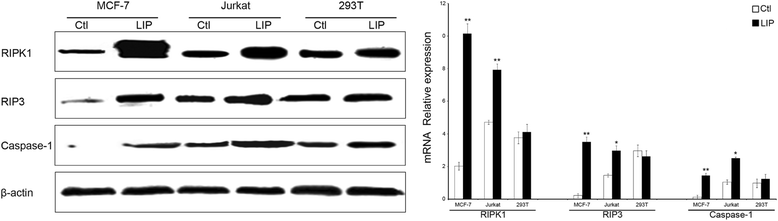
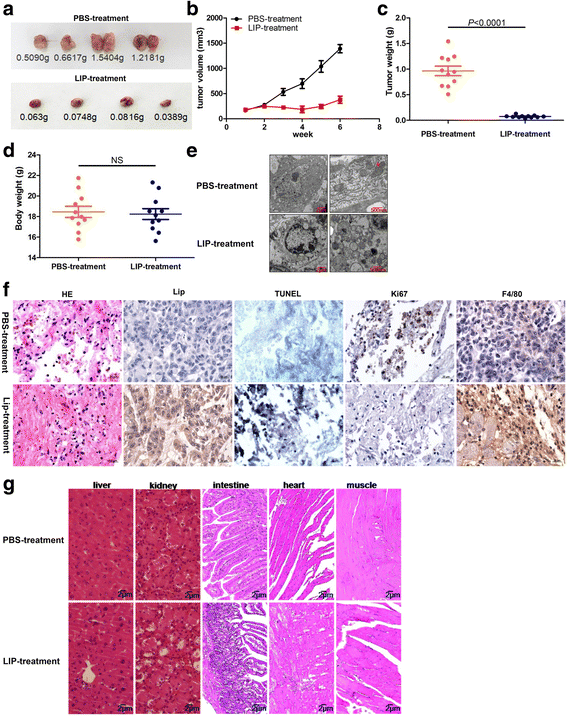
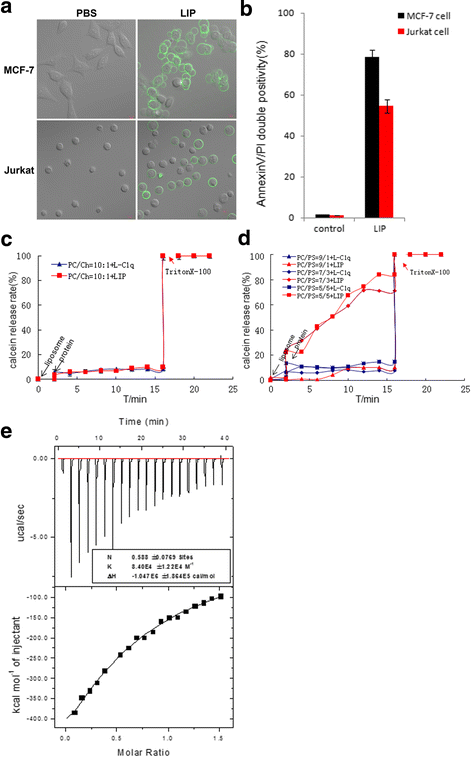
Results: LIP induces remarkable morphological changes in tumor cells, including cell blebbing, cytoskeletal alterations, mitochondrial fragmentation and endoplasmic reticulum vacuolation, and most of the cytoplasmic and organelle proteins are released following treatment with LIP. LIP evokes an elevation of intracellular calcium and inflammatory molecule levels. Our analysis of the cytotoxic mechanism suggests that LIP can upregulate the expression of caspase 1, RIPK1, RIP3 to trigger pyroptosis and necroptosis. To examine the effect of LIP in vivo, tumor xenograft experiments were performed, and the results indicated that LIP inhibits tumor growth without damage to mice. In addition, the cytotoxic action of LIP depended on the phosphatidylserine (PS) content of the cell membrane.
Conclusions: These observations suggest that LIP plays a crucial role in tumor cell survival and growth. The findings will also help to elucidate the mechanisms of host defense in lamprey.
Keywords: Cytotoxic activity; Inflammatory; LIP; Lamprey; Phosphatidylserine.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The animal experiments were performed in accordance with the regulations of the Animal Welfare and Research Ethics Committee of the Institute of Dalian Medical University’s Animal Care protocol (Permit Number: SCXK2008-0002).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Petranovic D, Pilcic G, Valkovic T, Sotosek Tokmadzic V, Laskarin G. Perforin- and granulysin-mediated cytotoxicity and interleukin 15 play roles in neurocognitive impairment in patients with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Med Hypotheses. 2014;83(1):122–126. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2014.03.024. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Apiratikul N, Penglong T, Suksen K, Svasti S, Chairoungdua A, Yingyongnarongkula B. In vitro delivery of curcumin with cholesterol-based cationic liposomes. Bioorg Khim. 2013;39(4):497–503. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

