Early effects of Epac depend on the fine-tuning of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ handling in cardiomyocytes
- PMID: 29037982
- PMCID: PMC5801154
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2017.10.005
Early effects of Epac depend on the fine-tuning of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ handling in cardiomyocytes
Abstract
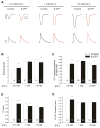
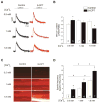
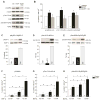
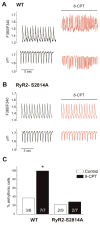
In cardiac muscle, signaling through cAMP governs many fundamental cellular functions, including contractility, relaxation and automatism. cAMP cascade leads to the activation of the classic protein kinase A but also to the stimulation of the recently discovered exchange protein directly activated by cAMP (Epac). The role of Epac in the regulation of intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis and contractility in cardiac myocytes is still matter of debate. In this study we showed that the selective Epac activator, 8-(4-chloro-phenylthio)-2'-O-methyladenosine-3', 5'-cyclic monophosphate (8-CPT), produced a positive inotropic effect when adult rat cardiac myocytes were stabilized at low [Ca2+]o (0.5mM), no changes at 1mM [Ca2+]o and a negative inotropic effect when [Ca2+]o was increased to 1.8mM. These effects were associated to parallel variations in sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) Ca2+ content. At all [Ca2+]o studied, 8-CPT induced an increase in Ca2+ spark frequency and enhanced CaMKII autophosphorylation and the CaMKII-dependent phosphorylation of SR proteins: phospholamban (PLN, at Thr17 site) and ryanodine receptor (RyR2, at Ser2814 site). We used transgenic mice lacking PLN CaMKII phosphorylation site (PLN-DM) and knock-in mice with an inactivated CaMKII site S2814 on RyR2 (RyR2-S2814A) to investigate the involvement of these processes in the effects of Epac stimulation. In PLN-DM mice, 8-CPT failed to induce the positive inotropic effect at low [Ca2+]o and RyR2-S2814A mice showed no propensity to arrhythmic events when compared to wild type mice myocytes. We conclude that stimulation of Epac proteins could have either beneficial or deleterious effects depending on the steady-state Ca2+ levels at which the myocyte is functioning, favoring the prevailing mechanism of SR Ca2+ handling (uptake vs. leak) in the different situations.
Keywords: CaMKII-dependent phosphorylations; Epac; Sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium handling.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Oestreich EA, Wang H, Malik S, Kaproth-Joslin KA, Blaxall BC, Kelley GG, Dirksen RT, Smrcka AV. Epac-mediated activation of phospholipase C(epsilon) plays a critical role in beta-adrenergic receptor-dependent enhancement of Ca2+ mobilization in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:5488–5495. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M608495200. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

