Delayed Maturation of Fast-Spiking Interneurons Is Rectified by Activation of the TrkB Receptor in the Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome
- PMID: 29038238
- PMCID: PMC5700416
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2893-16.2017
Delayed Maturation of Fast-Spiking Interneurons Is Rectified by Activation of the TrkB Receptor in the Mouse Model of Fragile X Syndrome
Abstract
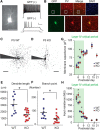
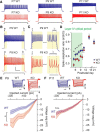
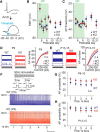
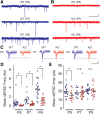
Fragile X syndrome (FXS) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that is a leading cause of inherited intellectual disability, and the most common known cause of autism spectrum disorder. FXS is broadly characterized by sensory hypersensitivity and several developmental alterations in synaptic and circuit function have been uncovered in the sensory cortex of the mouse model of FXS (Fmr1 KO). GABA-mediated neurotransmission and fast-spiking (FS) GABAergic interneurons are central to cortical circuit development in the neonate. Here we demonstrate that there is a delay in the maturation of the intrinsic properties of FS interneurons in the sensory cortex, and a deficit in the formation of excitatory synaptic inputs on to these neurons in neonatal Fmr1 KO mice. Both these delays in neuronal and synaptic maturation were rectified by chronic administration of a TrkB receptor agonist. These results demonstrate that the maturation of the GABAergic circuit in the sensory cortex is altered during a critical developmental period due in part to a perturbation in BDNF-TrkB signaling, and could contribute to the alterations in cortical development underlying the sensory pathophysiology of FXS.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Fragile X (FXS) individuals have a range of sensory related phenotypes, and there is growing evidence of alterations in neuronal circuits in the sensory cortex of the mouse model of FXS (Fmr1 KO). GABAergic interneurons are central to the correct formation of circuits during cortical critical periods. Here we demonstrate a delay in the maturation of the properties and synaptic connectivity of interneurons in Fmr1 KO mice during a critical period of cortical development. The delays both in cellular and synaptic maturation were rectified by administration of a TrkB receptor agonist, suggesting reduced BDNF-TrkB signaling as a contributing factor. These results provide evidence that the function of fast-spiking interneurons is disrupted due to a deficiency in neurotrophin signaling during early development in FXS.
Keywords: TrkB; critical period; fast-spiking interneuron; fragile X syndrome; somatosensory cortex; synapse.
Copyright © 2017 the authors 0270-6474/17/3711298-13$15.00/0.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
