Lipopolysaccharide Potentiates Insulin-Driven Hypoglycemic Shock
- PMID: 29038248
- PMCID: PMC5685187
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700820
Lipopolysaccharide Potentiates Insulin-Driven Hypoglycemic Shock
Abstract
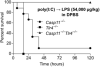
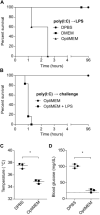
Critically ill patients typically present with hyperglycemia. Treatment with conventional insulin therapy (targeting 144-180 mg/dl) improves patient survival; however, intensive insulin therapy (IIT) targeting normal blood glucose levels (81-108 mg/dl) increases the incidence of moderate and severe hypoglycemia, and increases mortality. Septic patients are especially prone to IIT-induced hypoglycemia, but the mechanism remains unknown. Here, we show that codelivery of insulin with otherwise sublethal doses of LPS induced hypoglycemic shock in mice within 1-2 h. LPS impaired clearance of insulin, which amplified insulin receptor signaling. These effects were mediated by caspase-11, TLR4, and complement, each of which trigger eicosanoid production that potentiates insulin signaling. Finally, in an animal model of sepsis, we observed that Salmonella typhimurium-infected mice exhibited simultaneous impaired insulin clearance coexisting with insulin resistance. Our results raise the possibility that septic patients have impaired insulin clearance, which could increase their susceptibility to hypoglycemia during IIT, contraindicating its use.
Copyright © 2017 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures





References
-
- Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Janeway CA. A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll protein signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature. 1997;388:394–397. - PubMed
-
- Poltorak A, He X, Smirnova I, Liu MY, Van Huffel C, Du X, Birdwell D, Alejos E, Silva M, Galanos C, Freudenberg M, Ricciardi-Castagnoli P, Layton B, Beutler B. Defective LPS signaling in C3H/HeJ and C57BL/10ScCr mice: mutations in Tlr4 gene. Science. 1998;282:2085–2088. - PubMed
-
- Hoshino K, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Sanjo H, Ogawa T, Takeda Y, Takeda K, Akira S. Cutting edge: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-deficient mice are hyporesponsive to lipopolysaccharide: evidence for TLR4 as the Lps gene product. J Immunol. 1999;162:3749–3752. - PubMed
-
- Zhao L, Ohtaki Y, Yamaguchi K, Matsushita M, Fujita T, Yokochi T, Takada H, Endo Y. LPS-induced platelet response and rapid shock in mice: contribution of O-antigen region of LPS and involvement of the lectin pathway of the complement system. Blood. 2002;100:3233–3239. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

