Novel Gene Encoding 5-Aminosalicylate 1,2-Dioxygenase from Comamonas sp. Strain QT12 and Catalytic Properties of the Purified Enzyme
- PMID: 29038259
- PMCID: PMC5717158
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00395-17
Novel Gene Encoding 5-Aminosalicylate 1,2-Dioxygenase from Comamonas sp. Strain QT12 and Catalytic Properties of the Purified Enzyme
Abstract
The 1,125-bp mabB gene encoding 5-aminosalicylate (5ASA) 1,2-dioxygenase, a nonheme iron dioxygenase in the bicupin family that catalyzes the cleavage of the 5ASA aromatic ring to form cis-4-amino-6-carboxy-2-oxohexa-3,5-dienoate in the biodegradation of 3-aminobenzoate, was cloned from Comamonas sp. strain QT12 and characterized. The deduced amino acid sequence of the enzyme has low sequence identity with that of other reported ring-cleaving dioxygenases. MabB was heterologously expressed in Escherichia coli cells and purified as a His-tagged enzyme. The optimum pH and temperature for MabB are 8.0 and 10°C, respectively. FeII is required for the catalytic activity of the purified enzyme. The apparent Km and Vmax values of MabB for 5ASA are 52.0 ± 5.6 μM and 850 ± 33.2 U/mg, respectively. The two oxygen atoms incorporated into the product of the MabB-catalyzed reaction are both from the dioxygen molecule. Both 5ASA and gentisate could be converted by MabB; however, the catalytic efficiency of MabB for 5ASA was much higher (∼70-fold) than that for gentisate. The mabB-disrupted mutant lost the ability to grow on 3-aminobenzoate, and mabB expression was higher when strain QT12 was cultivated in the presence of 3-aminobenzoate. Thus, 5ASA is the physiological substrate of MabB.IMPORTANCE For several decades, 5-aminosalicylate (5ASA) has been advocated as the drug mesalazine to treat human inflammatory bowel disease and considered the key intermediate in the xenobiotic degradation of many aromatic organic pollutants. 5ASA biotransformation research will help us elucidate the microbial degradation of these pollutants. Most studies have reported that gentisate 1,2-dioxygenases (GDOs) can convert 5ASA with significantly high activity; however, the catalytic efficiency of these enzymes for gentisate is much higher than that for 5ASA. This study showed that MabB can convert 5ASA to cis-4-amino-6-carboxy-2-oxohexa-3,5-dienoate, incorporating two oxygen atoms from the dioxygen molecule into the product. Unlike GDOs, MabB uses 5ASA instead of gentisate as the primary substrate. mabB is the first reported 5-aminosalicylate 1,2-dioxygenase gene.
Keywords: 3-aminobenzoate; 5-aminosalicylate; Comamonas; biodegradation; dioxygenase.
Copyright © 2017 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures




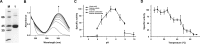


Similar articles
-
A novel gene, encoding 3-aminobenzoate 6-monooxygenase, involved in 3-aminobenzoate degradation in Comamonas sp. strain QT12.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Jun;102(11):4843-4852. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9015-4. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29696333
-
A novel 2-aminophenol 1,6-dioxygenase involved in the degradation of p-chloronitrobenzene by Comamonas strain CNB-1: purification, properties, genetic cloning and expression in Escherichia coli.Arch Microbiol. 2005 Jan;183(1):1-8. doi: 10.1007/s00203-004-0738-5. Epub 2004 Dec 3. Arch Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15580337
-
Function of different amino acid residues in the reaction mechanism of gentisate 1,2-dioxygenases deduced from the analysis of mutants of the salicylate 1,2-dioxygenase from Pseudaminobacter salicylatoxidans.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Oct;1854(10 Pt A):1425-37. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2015.06.005. Epub 2015 Jun 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 26093111
-
Oxygen activation by mononuclear nonheme iron dioxygenases involved in the degradation of aromatics.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2017 Apr;22(2-3):395-405. doi: 10.1007/s00775-017-1436-5. Epub 2017 Jan 13. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2017. PMID: 28084551 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ring-cleaving dioxygenases with a cupin fold.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012 Apr;78(8):2505-14. doi: 10.1128/AEM.07651-11. Epub 2012 Jan 27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22287012 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quantitative proteomic analysis of the microbial degradation of 3-aminobenzoic acid by Comamonas sp. QT12.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 20;12(1):17609. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-17570-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36266292 Free PMC article.
-
Label-Free Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of the Global Response to Indole-3-Acetic Acid in Newly Isolated Pseudomonas sp. Strain LY1.Front Microbiol. 2021 Aug 10;12:694874. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.694874. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34447357 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harayama S, Rekik M. 1989. Bacterial aromatic ring-cleavage enzymes are classified into two different gene families. J Biol Chem 264:15328–15333. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

