Specifically differentiated T cell subset promotes tumor immunity over fatal immunity
- PMID: 29038366
- PMCID: PMC5716032
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20170041
Specifically differentiated T cell subset promotes tumor immunity over fatal immunity
Abstract
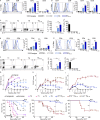
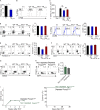
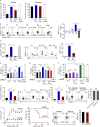
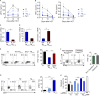
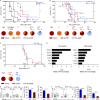
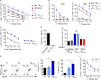
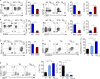
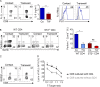
Allogeneic immune cells, particularly T cells in donor grafts, recognize and eliminate leukemic cells via graft-versus-leukemia (GVL) reactivity, and transfer of these cells is often used for high-risk hematological malignancies, including acute myeloid leukemia. Unfortunately, these cells also attack host normal tissues through the often fatal graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Full separation of GVL activity from GVHD has yet to be achieved. Here, we show that, in mice and humans, a population of interleukin-9 (IL-9)-producing T cells activated via the ST2-IL-33 pathway (T9IL-33 cells) increases GVL while decreasing GVHD through two opposing mechanisms: protection from fatal immunity by amphiregulin expression and augmentation of antileukemic activity compared with T9, T1, and unmanipulated T cells through CD8α expression. Thus, adoptive transfer of allogeneic T9IL-33 cells offers an attractive approach for separating GVL activity from GVHD.
© 2017 Ramadan et al.
Figures
References
-
- American Cancer Society 2015. Cancer Facts & Figures 2015. American Cancer Society, Atlanta: https://www.cancer.org/research/cancer-facts-statistics/all-cancer-facts....
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

