MCM2-regulated functional networks in lung cancer by multi-dimensional proteomic approach
- PMID: 29038488
- PMCID: PMC5643318
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-13440-x
MCM2-regulated functional networks in lung cancer by multi-dimensional proteomic approach
Abstract
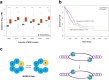
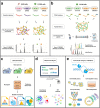
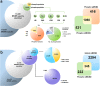
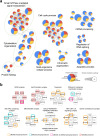
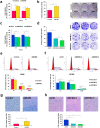
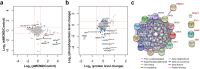
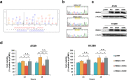
DNA replication control is vital for maintaining genome stability and the cell cycle, perhaps most notably during cell division. Malignancies often exhibit defective minichromosome maintenance protein 2 (MCM2), a cancer proliferation biomarker that serves as a licensing factor in the initiation of DNA replication. MCM2 is also known to be one of the ATPase active sites that facilitates conformational changes and drives DNA unwinding at the origin of DNA replication. However, the biological networks of MCM2 in lung cancer cells via protein phosphorylation remain unmapped. The RNA-seq datasets from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) revealed that MCM2 overexpression is correlated with poor survival rate in lung cancer patients. To uncover MCM2-regulated functional networks in lung cancer, we performed multi-dimensional proteomic approach by integrating analysis of the phosphoproteome and proteome, and identified a total of 2361 phosphorylation sites on 753 phosphoproteins, and 4672 proteins. We found that the deregulation of MCM2 is involved in lung cancer cell proliferation, the cell cycle, and migration. Furthermore, HMGA1S99 phosphorylation was found to be differentially expressed under MCM2 perturbation in opposite directions, and plays an important role in regulating lung cancer cell proliferation. This study therefore enhances our capacity to therapeutically target cancer-specific phosphoproteins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

