High-fidelity phenotyping: richness and freedom from bias
- PMID: 29040596
- PMCID: PMC7282504
- DOI: 10.1093/jamia/ocx110
High-fidelity phenotyping: richness and freedom from bias
Abstract
Electronic health record phenotyping is the use of raw electronic health record data to assert characterizations about patients. Researchers have been doing it since the beginning of biomedical informatics, under different names. Phenotyping will benefit from an increasing focus on fidelity, both in the sense of increasing richness, such as measured levels, degree or severity, timing, probability, or conceptual relationships, and in the sense of reducing bias. Research agendas should shift from merely improving binary assignment to studying and improving richer representations. The field is actively researching new temporal directions and abstract representations, including deep learning. The field would benefit from research in nonlinear dynamics, in combining mechanistic models with empirical data, including data assimilation, and in topology. The health care process produces substantial bias, and studying that bias explicitly rather than treating it as merely another source of noise would facilitate addressing it.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Medical Informatics Association.
Figures
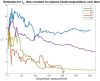
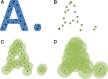
References
-
- Warner HR. Knowledge sectors for logical processing of patient data in the HELP system.Proc Annu Symp Comput Appl Med Care. 1978:401–04.
-
- Hripcsak G,Friedman C,Alderson PO,DuMouchel W,Johnson SB,Clayton PD. Unlocking clinical data from narrative reports: a study of natural language processing.Ann Intern Med. 1995;122:681–88. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

