Interferon-Alpha Reduces Human Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Increases Apoptosis via Activation of Distinct STAT1-Dependent Mechanisms
- PMID: 29040650
- PMCID: PMC5793815
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyx083
Interferon-Alpha Reduces Human Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Increases Apoptosis via Activation of Distinct STAT1-Dependent Mechanisms
Abstract
Background: In humans, interferon-α treatment for chronic viral hepatitis is a well-recognized clinical model for inflammation-induced depression, but the molecular mechanisms underlying these effects are not clear. Following peripheral administration in rodents, interferon-α induces signal transducer and activator of transcription-1 (STAT1) within the hippocampus and disrupts hippocampal neurogenesis.
Methods: We used the human hippocampal progenitor cell line HPC0A07/03C to evaluate the effects of 2 concentrations of interferon-α, similar to those observed in human serum during its therapeutic use (500 pg/mL and 5000 pg/mL), on neurogenesis and apoptosis.
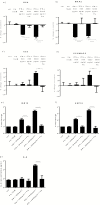
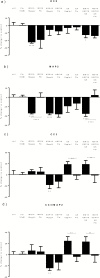
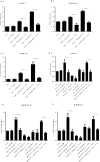
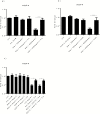
Results: Both concentrations of interferon-α decreased hippocampal neurogenesis, with the high concentration also increasing apoptosis. Moreover, interferon-α increased the expression of interferon-stimulated gene 15 (ISG15), ubiquitin-specific peptidase 18 (USP18), and interleukin-6 (IL-6) via activation of STAT1. Like interferon-α, co-treatment with a combination of ISG15, USP18, and IL-6 was able to reduce neurogenesis and enhance apoptosis via further downstream activation of STAT1. Further experiments showed that ISG15 and USP18 mediated the interferon-α-induced reduction in neurogenesis (potentially through upregulation of the ISGylation-related proteins UBA7, UBE2L6, and HERC5), while IL-6 mediated the interferon-α-induced increase in apoptosis (potentially through downregulation of aquaporin 4). Using transcriptomic analyses, we showed that interferon-α regulated pathways involved in oxidative stress and immune response (e.g., Nuclear Factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 [Nrf2] and interferon regulatory factor [IRF] signaling pathway), neuronal formation (e.g., CAMP response element-binding protein [CREB] signaling), and cell death regulation (e.g., tumor protein(p)53 signaling).
Conclusions: We identify novel molecular mechanisms mediating the effects of interferon-α on the human hippocampus potentially involved in inflammation-induced neuropsychiatric symptoms.
Keywords: apoptosis; depression; inflammation; interferon-alpha; neurogenesis.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Figures



References
-
- Alboni S, Gibellini L, Montanari C, Benatti C, Benatti S, Tascedda F, Brunello N, Cossarizza A, Pariante CM(2013)N-acetyl-cysteine prevents toxic oxidative effects induced by IFN-alpha in human neurons. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 16:1849–1865. - PubMed
-
- Anacker C, Cattaneo A, Luoni A, Musaelyan K, Zunszain PA, Milanesi E, Rybka J, Berry A, Cirulli F, Thuret S, Price J, Riva MA, Gennarelli M, Pariante CM (2013a) Glucocorticoid-related molecular signaling pathways regulating hippocampal neurogenesis. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:872–883. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anacker C, Cattaneo A, Musaelyan K, Zunszain PA, Horowitz M, Molteni R, Luoni A, Calabrese F, Tansey K, Gennarelli M, Thuret S, Price J, Uher R, Riva MA, Pariante CM (2013b) Role for the kinase SGK1 in stress, depression, and glucocorticoid effects on hippocampal neurogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:8708–8713. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

