RMBase v2.0: deciphering the map of RNA modifications from epitranscriptome sequencing data
- PMID: 29040692
- PMCID: PMC5753293
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx934
RMBase v2.0: deciphering the map of RNA modifications from epitranscriptome sequencing data
Abstract
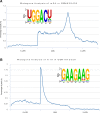
More than 100 distinct chemical modifications to RNA have been characterized so far. However, the prevalence, mechanisms and functions of various RNA modifications remain largely unknown. To provide transcriptome-wide landscapes of RNA modifications, we developed the RMBase v2.0 (http://rna.sysu.edu.cn/rmbase/), which is a comprehensive database that integrates epitranscriptome sequencing data for the exploration of post-transcriptional modifications of RNAs and their relationships with miRNA binding events, disease-related single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and RNA-binding proteins (RBPs). RMBase v2.0 was expanded with ∼600 datasets and ∼1 397 000 modification sites from 47 studies among 13 species, which represents an approximately 10-fold expansion when compared with the previous release. It contains ∼1 373 000 N6-methyladenosines (m6A), ∼5400 N1-methyladenosines (m1A), ∼9600 pseudouridine (Ψ) modifications, ∼1000 5-methylcytosine (m5C) modifications, ∼5100 2'-O-methylations (2'-O-Me), and ∼2800 modifications of other modification types. Moreover, we built a new module called 'Motif' that provides the visualized logos and position weight matrices (PWMs) of the modification motifs. We also constructed a novel module termed 'modRBP' to study the relationships between RNA modifications and RBPs. Additionally, we developed a novel web-based tool named 'modMetagene' to plot the metagenes of RNA modification along a transcript model. This database will help researchers investigate the potential functions and mechanisms of RNA modifications.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

