Societal preferences for adjuvant melanoma health states: UK and Australia
- PMID: 29041898
- PMCID: PMC5646133
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-017-3673-y
Societal preferences for adjuvant melanoma health states: UK and Australia
Abstract
Background: No studies have measured preference-based utility weights for specific toxicities and outcomes associated with approved and investigational adjuvant treatments for patients with resected high-risk melanoma.
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in the United Kingdom and Australia to obtain utilities for 14 adjuvant melanoma health states. One-on-one interviews were conducted using standard gamble; utility weights range from 0.0, dead, to 1.0, full health. Supplemental risk questions also were asked.
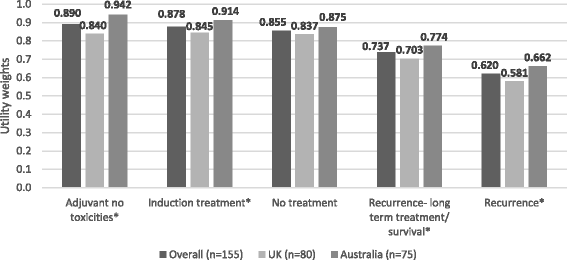
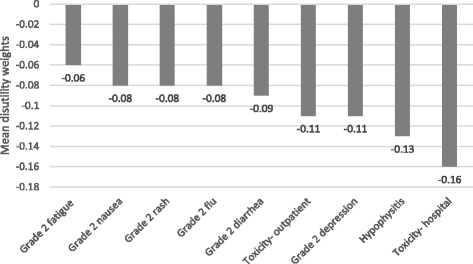
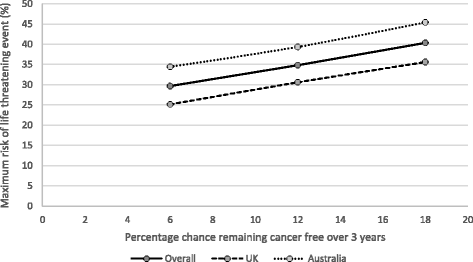
Results: Among 155 participants (52% male; mean age, 46 years) "adjuvant treatment no toxicities" (0.89) was most preferred, followed by "induction treatment" (0.88), and "no treatment" (0.86). Participants least preferred "cancer recurrence" (0.62); the utility for "cancer recurrence and 10-year survival with treatment" was 0.70. Disutilities for grade 2 toxicities ranged from -0.06 for fatigue to -0.13 for hypophysitis. The mean maximum acceptable risk of a life-threatening event ranged from 30% for a 6% increase in the chance of remaining cancer free over 3 years to 40% for an 18% increase; Australian respondents were willing to take higher risks.
Conclusion: Reproducible health utilities for adjuvant melanoma health states were obtained from the general population in two countries. These utilities can be incorporated into treatment-specific cost-effectiveness evaluations.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by Magil Institutional Review Board (Rockville, MD) and complied with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from all study participants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
MM: Consulting or Advisory Role: Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Clovis, GlaxoSmithKline, Immunocore (uncompensated), Merck, Roche (all compensated); Research Funding: Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Clovis, Eisai, GlaxoSmithKline, Immunocore, Medimmune, Merck, Pfizer, Roche, Vertex; Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Merck, Roche. MBA: Consulting or Advisory Role: Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Caladrius, GlaxoSmithKline, Genentech Roche, Merck, Nektar, Novartis, Pfizer. KA: Consulting role: Bristol-Myers Squibb. PFW: Employment: Bristol-Myers Squibb. SK: Employment: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Stock or Other Ownership: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Research Funding: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Travel, Accommodations, Expenses: Bristol-Myers Squibb. JS: Employment: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Stock or Other Ownership: Bristol-Myers Squibb; Research Funding: Bristol-Myers Squibb. KB: Consulting role: Bristol-Myers Squibb.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. http://www.who.int/uv/faq/skincancer/en/index1.html. Accessed 09 Dec 2015.
-
- Cancer Research UK. http://www.cancerresearchuk.org/health-professional/cancer-statistics/st.... Accessed 28 Sept 2015.
-
- Grob JJ, Jouary T, Dréno B, et al. Adjuvant therapy with pegylated interferon alfa-2b (36 months) versus low-dose interferon alfa-2b (18 months) in melanoma patients without macrometastatic nodes: an open-label, randomised, phase 3 European Association for Dermato-Oncology (EADO) study. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49(1):166–174. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2012.07.018. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical