Early coordinated rehabilitation in acute phase after hip fracture - a model for increased patient participation
- PMID: 29041916
- PMCID: PMC5646112
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-017-0640-z
Early coordinated rehabilitation in acute phase after hip fracture - a model for increased patient participation
Abstract
Background: Studies have shown that patients with hip fracture treated in a Comprehensive Geriatric Care (CGC) unit report better results in comparison to orthopaedic care. Furthermore, involving patients in their healthcare by encouraging patient participation can result in better quality of care and improved outcomes. To our knowledge no study has been performed comparing rehabilitation programmes within a CGC unit during the acute phase after hip fracture with focus on improving patients' perceived participation and subsequent effect on patients' function.
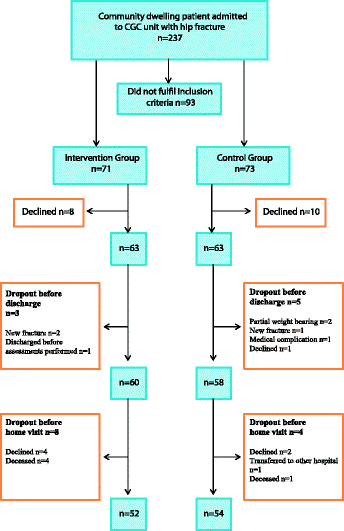
Methods: A prospective, controlled, intervention performed in a CGC unit and compared with standard care. A total of 126 patients with hip fracture were recruited who were prior to fracture; community dwelling, mobile indoors and independent in personal care. Intervention Group (IG): 63 patients, mean age 82.0 years and Control Group (CG): 63 patients mean age 80.5 years.
Intervention: coordinated rehabilitation programme with early onset of patient participation and intensified occupational therapy and physiotherapy after hip fracture surgery. The primary outcome measure was self-reported patient participation at discharge. Secondary outcome measures were: TLS-BasicADL; Bergs Balance Scale (BBS); Falls Efficacy Scale FES(S); Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB) and Timed Up and Go (TUG) at discharge and 1 month and ADL staircase for instrumental ADL at 1 month.
Results: At discharge a statistically significant greater number of patients in the IG reported higher levels of participation (p < 0.05) and independence in lower body hygiene (p < 0.05) and dressing (p < 0.001). There were however no statistically significant differences at discharge and 1 month between groups in functional balance and confidence, performance measures or risk for falls.
Conclusion: This model of OT and PT coordinated inpatient rehabilitation had a positive effect on patients' perceived participation in their rehabilitation and ADL at discharge but did not appear to affect level of recovery or risk for future falls at 1 month. A large proportion of patients remained at risk for future falls at 1 month in both groups highlighting the need for continued rehabilitation after discharge.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT03301584 (Retrospectively registered: 4th October 2017).
Keywords: Adl; Functional balance; Hip fracture; Patient participation; Physical performance.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Regional Ethics Board at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, dnr 541–13. Patients were given written and verbal information regarding the study and gave their written consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Kronborg L, Bandholm T, Palm H, Kehlet H, Kristensen MT. Effectiveness of acute in-hospital physiotherapy with knee-extension strength training in reducing strength deficits in patients with a hip fracture: a randomised controlled trial. PLoS One. 2017;12(6):e0179867. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179867. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous