Incretins in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 29041949
- PMCID: PMC5645916
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-017-1431-9
Incretins in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: The precise mechanism linking systemic inflammation with insulin resistance (IR) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) remains elusive. In the present study, we determined whether the incretin-insulin axis and incretin effect are disrupted in patients with RA and if they are related to the IR found in these patients.
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study that encompassed 361 subjects without diabetes, 151 patients with RA, and 210 sex-matched control subjects. Insulin, C-peptide, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP), dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) soluble form, and IR indexes by homeostatic model assessment (HOMA2) were assessed. A multivariable analysis adjusted for IR-related factors was performed. Additionally, ten patients and ten control subjects underwent a 566-kcal meal test so that we could further study the postprandial differences of these molecules between patients and control subjects.
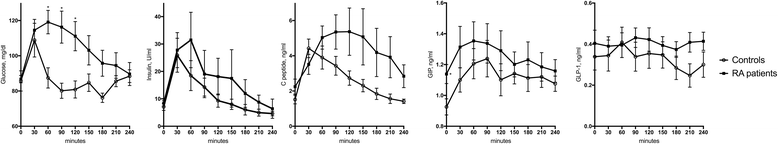
Results: Insulin, C-peptide, and HOMA2-IR indexes were higher in patients than in control subjects. This was also the case for GLP-1 (0.49 ± 1.28 vs. 0.71 ± 0.22 ng/ml, p = 0.000) and GIP (0.37 ± 0.40 vs. 1.78 ± 0.51 ng/ml, p = 0.000). These differences remained significant after multivariable adjustment including glucocorticoid intake. Disease Activity Score in 28 joints with erythrocyte sedimentation rate (β coefficient 46, 95% CI 6-87, p = 0.026) and Clinical Disease Activity Index (β coefficient 7.74, 95% CI 1.29-14.20, p = 0.019) were associated with DPP-4 serum levels. GLP-1 positively correlated with β-cell function (HOMA2 of β-cell production calculated with C-peptide) in patients but not in control subjects (interaction p = 0.003). The meal test in patients with RA revealed a higher total and late response AUC for glucose response, a later maximal response of C-peptide, and a flatter curve in GIP response.
Conclusions: The incretin-insulin axis, both during fasting and postprandial, is impaired in patients with RA.
Keywords: Incretins; Insulin resistance; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol was approved by the institutional review committees at Hospital Universitario de Canarias and Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla (both in Spain), and all subjects provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Plasma Incretin Levels and Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Activity in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016 Aug;13(8):1378-87. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201510-697OC. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2016. PMID: 27104640
-
Increased postprandial GIP and glucagon responses, but unaltered GLP-1 response after intervention with steroid hormone, relative physical inactivity, and high-calorie diet in healthy subjects.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011 Feb;96(2):447-53. doi: 10.1210/jc.2010-1605. Epub 2010 Nov 3. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2011. PMID: 21047927
-
Comparative effects of variations in duodenal glucose load on glycemic, insulinemic, and incretin responses in healthy young and older subjects.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Mar;97(3):844-51. doi: 10.1210/jc.2011-2583. Epub 2012 Jan 11. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22238398 Clinical Trial.
-
[Incretin hormones in the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Part I: influence of insulinotropic gut-derived hormones (incretins) on glucose metabolism].Endokrynol Pol. 2007 Nov-Dec;58(6):522-8. Endokrynol Pol. 2007. PMID: 18205109 Review. Polish.
-
Effect of Systemic Inflammation on the Function of Insulin and Glucose Metabolism in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2015;12(2):156-62. doi: 10.2174/1573399811666150602150325. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2015. PMID: 26033386 Review.
Cited by
-
Insulin Signaling in Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 30;12:672519. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.672519. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33995414 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apolipoprotein C-III is linked to the insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction that are present in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 May 30;24(1):126. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02822-w. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35637531 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of disease activity on impaired glucose metabolism in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2021 Mar 26;23(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s13075-021-02476-0. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 33771189 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes and Osteoarthritis: Exploring the Interactions and Therapeutic Implications of Insulin, Metformin, and GLP-1-Based Interventions.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 23;12(8):1630. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081630. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39200096 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic and therapeutic links between rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes mellitus.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Jun;23(2):287-299. doi: 10.1007/s10238-022-00816-1. Epub 2022 Mar 20. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 35306615 Review.
References
-
- Mentlein R, Gallwitz B, Schmidt WE. Dipeptidyl-peptidase IV hydrolyses gastric inhibitory polypeptide, glucagon-like peptide-1(7–36)amide, peptide histidine methionine and is responsible for their degradation in human serum. Eur J Biochem. 1993;214(3):829–835. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17986.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Deacon CF, Johnsen AH, Holst JJ. Degradation of glucagon-like peptide-1 by human plasma in vitro yields an N-terminally truncated peptide that is a major endogenous metabolite in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1995;80(3):952–957. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous