Linc-RoR promotes MAPK/ERK signaling and confers estrogen-independent growth of breast cancer
- PMID: 29041978
- PMCID: PMC5645922
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-017-0727-3
Linc-RoR promotes MAPK/ERK signaling and confers estrogen-independent growth of breast cancer
Abstract
Background: The conversion from estrogen-dependent to estrogen-independent state of ER+ breast cancer cells is the key step to promote resistance to endocrine therapies. Although the crucial role of MAPK/ERK signaling pathway in estrogen-independent breast cancer cell growth is well established, the underlying mechanism is not fully understood.
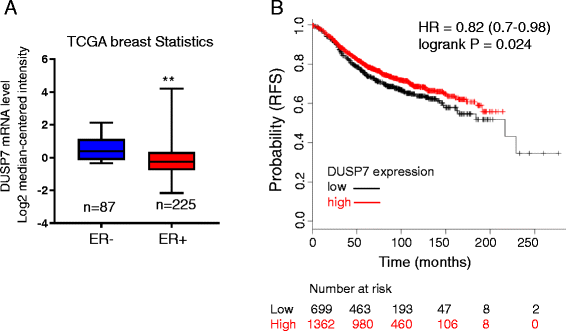
Methods: In this study, we profiled lncRNA expression against a focused group of lncRNAs selected from lncRNA database. CRISPR/Cas9 was employed to knockout (KO) linc-RoR in MCF-7 cells, while rescue experiments were carried out to re-express linc-RoR in KO cells. Colony formation and MTT assays were used to examine the role of linc-RoR in estrogen-independent growth and tamoxifen resistance. Western blot and qRT-PCR were used to determine the change of protein and lncRNA levels, respectively. The expression of DUSP7 in clinical specimens was downloaded from Oncomine ( www.oncomine.org ) and the dataset from Kaplan-Meier Plotter ( http://kmplot.com ) was used to analyze the clinical outcomes in relation to DUSP7.
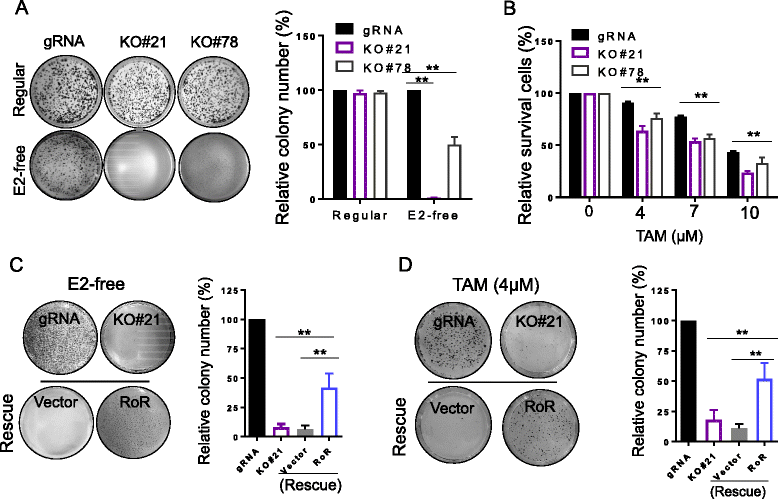
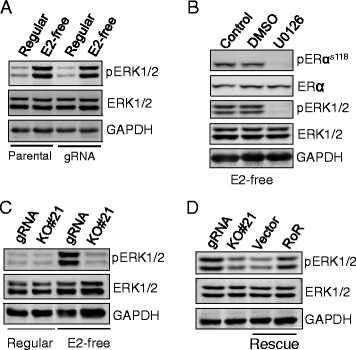
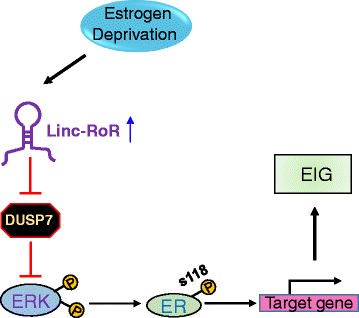
Results: We identified that linc-RoR functions as an onco-lncRNA to promote estrogen-independent growth of ER+ breast cancer. Under estrogen deprivation, linc-RoR causes the upregulation of phosphorylated MAPK/ERK pathway which in turn activates ER signaling. Knockout of linc-RoR abrogates estrogen deprivation-induced ERK activation as well as ER phosphorylation, whereas re-expression of linc-RoR restores all above phenotypes. Moreover, we show that the ERK-specific phosphatase Dual Specificity Phosphatase 7 (DUSP7), also known as MKP-X, is involved in linc-RoR KO-induced repression of MAPK/ERK signaling. Interestingly, linc-RoR KO increases the protein stability of DUSP7, resulting in repression of ERK phosphorylation. Clinical data analysis reveal that DUSP7 expression is lower in ER+ breast cancer samples than that in ER- breast cancer. Moreover, downregulation of DUSP7 expression is associated with poor patient survival.
Conclusion: Taken together, these results suggest that linc-RoR promotes estrogen-independent growth and activation of MAPK/ERK pathway of breast cancer cells by regulating the ERK-specific phosphatase DUSP7. Thus, this study might help not only in establishing a role for linc-RoR in estrogen-independent and tamoxifen resistance of ER+ breast cancer, but also suggesting a link between linc-RoR and MAPK/ERK pathway.
Keywords: Breast cancer; DUSP7; ERK; Estrogen-independent growth; Linc-RoR.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Inhibitory role of large intergenic noncoding RNA-ROR on tamoxifen resistance in the endocrine therapy of breast cancer by regulating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Feb;234(2):1904-1912. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27066. Epub 2018 Aug 26. J Cell Physiol. 2019. Retraction in: J Cell Physiol. 2022 Mar;237(3):2004. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30516. PMID: 30145819 Retracted.
-
Linc-ROR promotes the progression of breast cancer and decreases the sensitivity to rapamycin through miR-194-3p targeting MECP2.Mol Oncol. 2020 Sep;14(9):2231-2250. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12700. Epub 2020 May 24. Mol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32335998 Free PMC article.
-
Acquisition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in the tamoxifen-resistant breast cancer cell: a new role for G protein-coupled estrogen receptor in mediating tamoxifen resistance through cancer-associated fibroblast-derived fibronectin and β1-integrin signaling pathway in tumor cells.Breast Cancer Res. 2015 May 21;17(1):69. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0579-y. Breast Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25990368 Free PMC article.
-
A review on the importance of LINC-ROR in human disorders.Pathol Res Pract. 2023 Apr;244:154420. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2023.154420. Epub 2023 Mar 18. Pathol Res Pract. 2023. PMID: 36989849 Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs as Mediators of Tamoxifen Resistance in Breast Cancers.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1152:229-241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-20301-6_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31456186 Review.
Cited by
-
LncRNA XLOC_015548 affects the proliferation and differentiation of myoblasts via the MAPK signaling pathway.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023 Mar;248(6):469-480. doi: 10.1177/15353702231151963. Epub 2023 Feb 27. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2023. PMID: 36852460 Free PMC article.
-
Tamoxifen resistance-related ceRNA network for breast cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Nov 25;10:1023079. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1023079. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36506097 Free PMC article.
-
LINC00346 promotes pancreatic cancer progression through the CTCF-mediated Myc transcription.Oncogene. 2019 Oct;38(41):6770-6780. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-0918-z. Epub 2019 Aug 7. Oncogene. 2019. PMID: 31391552
-
Functional Relationships between Long Non-Coding RNAs and Estrogen Receptor Alpha: A New Frontier in Hormone-Responsive Breast Cancer Management.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 6;24(2):1145. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021145. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long noncoding RNA ROR as a novel biomarker for progress and prognosis outcome in human cancer: a meta-analysis in the Asian population.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Oct 15;10:4641-4652. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S174143. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 30410399 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mancuso MR, Massarweh SA. Endocrine therapy and strategies to overcome therapeutic resistance in breast cancer. Curr Probl Cancer. 2016; - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

