PAK5-mediated phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of NF-κB-p65 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo
- PMID: 29041983
- PMCID: PMC5645986
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-017-0610-5
PAK5-mediated phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of NF-κB-p65 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo
Abstract
Background: Abnormal proliferation is significantly associated with the promotion of malignant tumor. Growing evidence suggest that the signal pathways of p21cdc42/rac1-activated kinase 5 (PAK5) have been found in various tumor progression, however, the role of PAK5 in breast cancer remains largely unclear.
Methods: We evaluated PAK5 and p65 staining in breast cancer tissues (BCTs) and paired non-cancerous tissues (NTs) using tissue microarray (TMA) technology. The functions of PAK5 were studied in vitro and in vivo. Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and flow cytometry were performed to determine proliferation of breast cancer cells. Phosphorylation assay and co-immunoprecipitation (co-IP) were employed to identify the regulation mechanism of p65 by PAK5. The activation of Cyclin D1 promoter was measured with luciferase reporter assay. Xenograft models in nude mice were established to explore the roles of PAK5 in breast cancer growth.
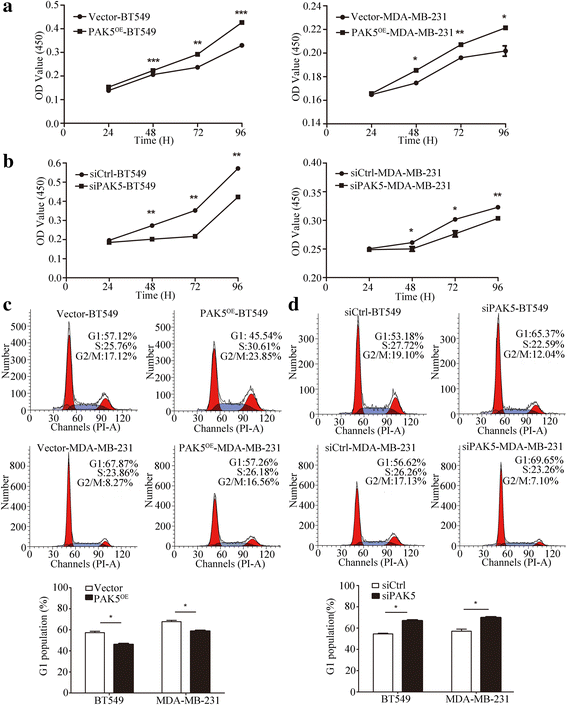
Results: In this study, we show that PAK5 is highly expressed in breast cancer tissues and the increased PAK5 is significantly associated with breast cancer progression. Overexpression of PAK5 promotes the proliferation and cell-cycle progression by increasing the expression of Cyclin D1 in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistic studies demonstrated that PAK5 can promote the phosphorylation and the nuclear translocation of p65 subunit of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB). Furthermore, p65 can directly bind to the promoter of Cyclin D1 and mediate an increase in its protein expression.
Conclusions: Taken together, our findings suggest that PAK5 may serve as a potential prognosis marker and therapeutic target for human breast cancer.
Keywords: Cell proliferation; Cyclin D1; PAK5; p65.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval
This study was performed under a protocol approved by the Review Board of the Affliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, and all examinations were performed after obtaining written informed consents. Animal experiments were in conformance with the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Xuzhou Medical University.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures





Similar articles
-
PAK5-mediated AIF phosphorylation inhibits its nuclear translocation and promotes breast cancer tumorigenesis.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Mar 27;17(5):1315-1327. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.58102. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33867848 Free PMC article.
-
Sphk1 promotes breast epithelial cell proliferation via NF-κB-p65-mediated cyclin D1 expression.Oncotarget. 2016 Dec 6;7(49):80579-80585. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13013. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27811358 Free PMC article.
-
PAK5-mediated E47 phosphorylation promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of colon cancer.Oncogene. 2016 Apr 14;35(15):1943-54. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.259. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26212009
-
Human p21-activated kinase 5 (PAK5) expression and potential mechanisms in relevant cancers: Basic and clinical perspectives for molecular cancer therapeutics.Life Sci. 2020 Jan 15;241:117113. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.117113. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 31805288 Review.
-
An oncogenic kinase: putting PAK5 forward.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014 Jul;18(7):807-15. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2014.918103. Epub 2014 May 29. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2014. PMID: 24869804 Review.
Cited by
-
NF-κB in inflammation and cancer.Cell Mol Immunol. 2025 Aug;22(8):811-839. doi: 10.1038/s41423-025-01310-w. Epub 2025 Jun 25. Cell Mol Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40562870 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p21-Activated Kinase: Role in Gastrointestinal Cancer and Beyond.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 28;14(19):4736. doi: 10.3390/cancers14194736. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36230657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PAK5-mediated AIF phosphorylation inhibits its nuclear translocation and promotes breast cancer tumorigenesis.Int J Biol Sci. 2021 Mar 27;17(5):1315-1327. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.58102. eCollection 2021. Int J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33867848 Free PMC article.
-
miR‑489 promotes apoptosis and inhibits invasiveness of glioma cells by targeting PAK5/RAF1 signaling pathways.Oncol Rep. 2019 Dec;42(6):2390-2401. doi: 10.3892/or.2019.7381. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Oncol Rep. 2019. Retraction in: Oncol Rep. 2023 Jun;49(6):127. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8564. PMID: 31638257 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Nuclear factor-kappa B-dependent X-box binding protein 1 signalling promotes the proliferation of nucleus pulposus cells under tumour necrosis factor alpha stimulation.Cell Prolif. 2019 Mar;52(2):e12542. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12542. Epub 2018 Nov 14. Cell Prolif. 2019. PMID: 30430692 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

