Survival Outcomes of Men with Lymph Node-positive Prostate Cancer After Radical Prostatectomy: A Comparative Analysis of Different Postoperative Management Strategies
- PMID: 29042125
- PMCID: PMC6049832
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.09.027
Survival Outcomes of Men with Lymph Node-positive Prostate Cancer After Radical Prostatectomy: A Comparative Analysis of Different Postoperative Management Strategies
Abstract
Background: Optimal management of patients with lymph node metastasis (LNM) after radical prostatectomy (RP) remains undefined.
Objective: We evaluated the association between three different management strategies and survival in prostate cancer with LNM after RP.
Design, setting, and participants: We analyzed data of 1338 patients with LNM after RP from three tertiary care centers. Three hundred and eighty-seven patients (28%) were observed, 676 (49%) received lifelong adjuvant androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), and 325 (23%) received adjuvant external beam radiation therapy (EBRT) and ADT. Three hundred and sixty-eight men were followed for more than 10 yr.
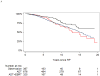
Outcome measurements and statistical analysis: Primary outcome measure was overall survival (OS). Secondary outcomes were cancer-specific survival (CSS) and other-cause mortality. Kaplan-Meier methods were used to visualize OS for the three treatment groups. Cox proportional hazards regression was utilized to compare OS and CSS among the three groups.
Results and limitations: ADT+EBRT was associated with better OS than ADT alone (hazard ratio [HR]: 0.46, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.32-0.66, p<0.0001) or observation (HR: 0.41, 95% CI: 0.27-0.64, p<0.0001). Higher-risk patients benefited more from ADT+EBRT than lower-risk patients. Ten-year mortality risk difference between ADT+EBRT, observation, or ADT alone ranged from 5% in low-risk patients to 40% in high-risk patients. Adjuvant ADT+EBRT was also associated with better CSS than observation or ADT alone (p<0.0001), ADT had better CSS compared to observation (HR: 0.64, 95% CI: 0.43-0.95, p=0.027). However, ADT was associated with an increased risk of other-cause mortality (HR: 3.05, 95% CI: 1.45-6.40, p=0.003) compared with observation, resulting in similar OS between ADT and observation (HR: 0.90, 95% CI: 0.65-1.25, p=0.5). While selection bias might remain, its effect would operate in the opposite direction to our findings.
Conclusions: In men with LNM after RP, ADT+EBRT improved survival over either observation or adjuvant ADT alone. This survival benefit increases with higher-risk disease.
Patient summary: Lymph node metastasis following radical prostatectomy is associated with poor survival outcomes. However, we found that adjuvant androgen deprivation therapy with external beam radiation therapy improved survival in these patients.
Keywords: Adjuvant radiotherapy; Antineoplastic agents; Hormonal; Lymphatic metastasis; Mortality; Prognosis; Prostatectomy; Prostatic neoplasms.
Copyright © 2017 European Association of Urology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures


Comment in
-
Nodal Metastases at Radical Prostatectomy: More Aggressive Disease Warrants Consideration of Multimodal Treatment.Eur Urol. 2018 Jun;73(6):897-898. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.11.030. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Eur Urol. 2018. PMID: 29224914 No abstract available.
-
Re: Karim A. Touijer, Robert Jeffery Karnes, Niccolo Passoni, et al. Survival Outcomes of Men with Lymph Node-positive Prostate Cancer After Radical Prostatectomy: A Comparative Analysis of Different Postoperative Management Strategies. Eur Urol 2018;73:890-6.Eur Urol. 2018 Jul;74(1):e15-e17. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.04.001. Epub 2018 Apr 13. Eur Urol. 2018. PMID: 29661485 No abstract available.
-
Reply to Pim J. van Leeuwen and Henk G. van der Poel's Letter to the Editor re: Karim A. Touijer, Robert J. Karnes, Niccolo Passoni, et al. Survival Outcomes of Men with Lymph Node-positive Prostate Cancer After Radical Prostatectomy: A Comparative Analysis of Different Postoperative Management Strategies. Eur Urol 2018;73:890-6.Eur Urol. 2018 Jul;74(1):e18-e19. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2018.04.002. Eur Urol. 2018. PMID: 29691082 No abstract available.
References
-
- Abdollah F, Karnes RJ, Suardi N, et al. Impact of adjuvant radiotherapy on survival of patients with node-positive prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:3939–47. - PubMed
-
- Messing EM, Manola J, Sarosdy M, Wilding G, Crawford D, Trump D. Immediate hormonal therapy compared with observation after radical prostatectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy in men with node-positive prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:1781–8. - PubMed
-
- Touijer KA, Mazzola CR, Sjoberg DD, Scardino PT, Eastham JA. Long-term outcomes of patients with lymph node metastasis treated with radical prostatectomy without adjuvant androgen-deprivation therapy. Eur Urol. 2014;65:20–5. - PubMed
-
- Boorjian SA, Thompson RH, Siddiqui S, et al. Long-term outcome after radical prostatectomy for patients with lymph node positive prostate cancer in the prostate specific antigen era. J Urol. 2007;178:864–70. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

