Regulating the regulators: Epigenetic, transcriptional, and post-translational regulation of RGS proteins
- PMID: 29042285
- PMCID: PMC5732043
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.10.007
Regulating the regulators: Epigenetic, transcriptional, and post-translational regulation of RGS proteins
Abstract
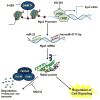
Regulators of G protein signaling (RGS) are a family of proteins classically known to accelerate the intrinsic GTPase activity of G proteins, which results in accelerated inactivation of heterotrimeric G proteins and inhibition of G protein coupled receptor signaling. RGS proteins play major roles in essential cellular processes, and dysregulation of RGS protein expression is implicated in multiple diseases, including cancer, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases. The expression of RGS proteins is highly dynamic and is regulated by epigenetic, transcriptional and post-translational mechanisms. This review summarizes studies that report dysregulation of RGS protein expression in disease states, and presents examples of drugs that regulate RGS protein expression. Additionally, this review discusses, in detail, the transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms regulating RGS protein expression, and further assesses the therapeutic potential of targeting these mechanisms. Understanding the molecular mechanisms controlling the expression of RGS proteins is essential for the development of therapeutics that indirectly modulate G protein signaling by regulating expression of RGS proteins.
Keywords: Epigenetics; MicroRNA; Post-translational modification; Proteasomal degradation; RGS; Regulator of G protein signaling; Therapeutics; Transcription factors.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

