Mechanisms of μ-opioid receptor inhibition of NMDA receptor-induced substance P release in the rat spinal cord
- PMID: 29042318
- PMCID: PMC5726399
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.10.014
Mechanisms of μ-opioid receptor inhibition of NMDA receptor-induced substance P release in the rat spinal cord
Abstract
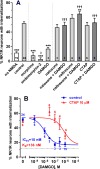
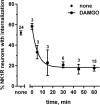
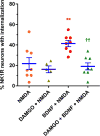
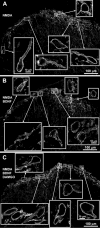
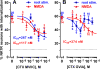
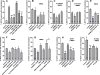
The interaction between NMDA receptors and μ-opioid receptors in primary afferent terminals was studied by using NMDA to induce substance P release, measured as neurokinin 1 receptor internalization. In rat spinal cord slices, the μ-opioid receptor agonists morphine, DAMGO and endomorphin-2 inhibited NMDA-induced substance P release, whereas the antagonist CTAP right-shifted the concentration response of DAMGO. In vivo, substance P release induced by intrathecal NMDA after priming with BDNF was inhibited by DAMGO. ω-Conotoxins MVIIC and GVIA inhibited about half of the NMDA-induced substance P release, showing that it was partially mediated by the opening of voltage-gated calcium (Cav) channels. In contrast, DAMGO or ω-conotoxins did not inhibit capsaicin-induced substance P release. In cultured DRG neurons, DAMGO but not ω-conotoxin inhibited NMDA-induced increases in intracellular calcium, indicating that μ-opioid receptors can inhibit NMDA receptor function by mechanisms other than inactivation of Cav channels. Moreover, DAMGO decreased the ω-conotoxin-insensitive component of the substance P release. Potent inhibition by ifenprodil showed that these NMDA receptors have the NR2B subunit. Activators of adenylyl cyclase and protein kinase A (PKA) induced substance P release and this was decreased by the NMDA receptor blocker MK-801 and by DAMGO. Conversely, inhibitors of adenylyl cyclase and PKA, but not of protein kinase C, decreased NMDA-induced substance P release. Hence, these NMDA receptors are positively modulated by the adenylyl cyclase-PKA pathway, which is inhibited by μ-opioid receptors. In conclusion, μ-opioid receptors inhibit NMDA receptor-induced substance P release through Cav channel inactivation and adenylyl cyclase inhibition.
Keywords: BVT948 (PubChem CID: 6604934); CTAP (PubChem CID: 90479802); Calcium channel; DAMGO (PubChem CID: 5462471); Endomorphin-2 (PubChem CID: 5311081); KT5720 (PubChem CID: 454202); Mu-opioid receptor; NMDA (PubChem CID: 22880); NMDA receptor; Neurokinin 1 receptor; Primary afferent; Protein kinase A; SQ22536 (PubChem CID: 5270); d-serine (PubChem CID: 71077); ω-conotoxin GVIA (PubChem CID: 73169082); ω-conotoxin MVIIC (PubChem CID: 56841670).
Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures


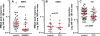

References
-
- Aimone LD, Yaksh TL. Opioid modulation of capsaicin-evoked release of substance P from rat spinal cord in vivo. Peptides. 1989;10:1127–1131. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

