Plastic Transcriptomes Stabilize Immunity to Pathogen Diversity: The Jasmonic Acid and Salicylic Acid Networks within the Arabidopsis/ Botrytis Pathosystem
- PMID: 29042403
- PMCID: PMC5728128
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.17.00348
Plastic Transcriptomes Stabilize Immunity to Pathogen Diversity: The Jasmonic Acid and Salicylic Acid Networks within the Arabidopsis/ Botrytis Pathosystem
Abstract
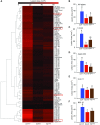
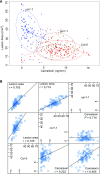
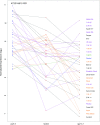
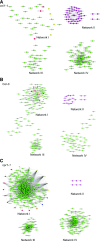
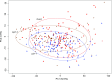
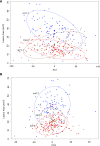
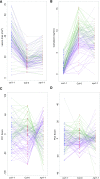
To respond to pathogen attack, selection and associated evolution has led to the creation of plant immune system that are a highly effective and inducible defense system. Central to this system are the plant defense hormones jasmonic acid (JA) and salicylic acid (SA) and crosstalk between the two, which may play an important role in defense responses to specific pathogens or even genotypes. Here, we used the Arabidopsis thaliana-Botrytis cinerea pathosystem to test how the host's defense system functions against genetic variation in a pathogen. We measured defense-related phenotypes and transcriptomic responses in Arabidopsis wild-type Col-0 and JA- and SA-signaling mutants, coi1-1 and npr1-1, individually challenged with 96 diverse B. cinerea isolates. Those data showed genetic variation in the pathogen influences on all components within the plant defense system at the transcriptional level. We identified four gene coexpression networks and two vectors of defense variation triggered by genetic variation in B. cinerea This showed that the JA and SA signaling pathways functioned to constrain/canalize the range of virulence in the pathogen population, but the underlying transcriptomic response was highly plastic. These data showed that plants utilize major defense hormone pathways to buffer disease resistance, but not the metabolic or transcriptional responses to genetic variation within a pathogen.
© 2017 American Society of Plant Biologists. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- An B., Li B., Qin G., Tian S. (2015). Function of small GTPase Rho3 in regulating growth, conidiation and virulence of Botrytis cinerea Fungal Genet. Biol. 75: 46–55. - PubMed
-
- Bednarek P., Piślewska-Bednarek M., Ver Loren van Themaat E., Maddula R.K., Svatoš A., Schulze-Lefert P. (2011). Conservation and clade-specific diversification of pathogen-inducible tryptophan and indole glucosinolate metabolism in Arabidopsis thaliana relatives. New Phytol. 192: 713–726. - PubMed
-
- Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. A Stat. Soc. 57: 289–300.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

