Transcription factor 19 interacts with histone 3 lysine 4 trimethylation and controls gluconeogenesis via the nucleosome-remodeling-deacetylase complex
- PMID: 29042441
- PMCID: PMC5733577
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.786863
Transcription factor 19 interacts with histone 3 lysine 4 trimethylation and controls gluconeogenesis via the nucleosome-remodeling-deacetylase complex
Abstract
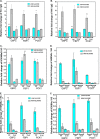
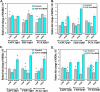
Transcription factor 19 (TCF19) has been reported as a type 1 diabetes-associated locus involved in maintenance of pancreatic β cells through a fine-tuned regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis. TCF19 also exhibits genomic association with type 2 diabetes, although the precise molecular mechanism remains unknown. It harbors both a plant homeodomain and a forkhead-associated domain implicated in epigenetic recognition and gene regulation, a phenomenon that has remained unexplored. Here, we show that TCF19 selectively interacts with histone 3 lysine 4 trimethylation through its plant homeodomain finger. Knocking down TCF19 under high-glucose conditions affected many metabolic processes, including gluconeogenesis. We found that TCF19 overexpression represses de novo glucose production in HepG2 cells. The transcriptional repression of key genes, induced by TCF19, coincided with NuRD (nucleosome-remodeling-deacetylase) complex recruitment to the promoters of these genes. TCF19 interacted with CHD4 (chromodomain helicase DNA-binding protein 4), which is a part of the NuRD complex, in a glucose concentration-independent manner. In summary, our results show that TCF19 interacts with an active transcription mark and recruits a co-repressor complex to regulate gluconeogenic gene expression in HepG2 cells. Our study offers critical insights into the molecular mechanisms of transcriptional regulation of gluconeogenesis and into the roles of chromatin readers in metabolic homeostasis.
Keywords: PHD finger; gene transcription; gluconeogenesis; glucose metabolism; histone H3 lysine 4 trimethylation; histone deacetylation; histone modification; nucleosome remodeling deacetylase (NuRD); transcription factor; transcription repressor.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

