In vitro reconstitution of T cell receptor-mediated segregation of the CD45 phosphatase
- PMID: 29042512
- PMCID: PMC5676914
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1710358114
In vitro reconstitution of T cell receptor-mediated segregation of the CD45 phosphatase
Abstract
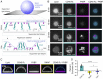
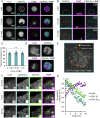
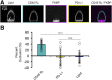
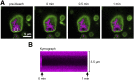
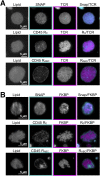
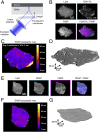
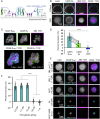
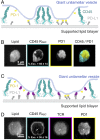
T cell signaling initiates upon the binding of peptide-loaded MHC (pMHC) on an antigen-presenting cell to the T cell receptor (TCR) on a T cell. TCR phosphorylation in response to pMHC binding is accompanied by segregation of the transmembrane phosphatase CD45 away from TCR-pMHC complexes. The kinetic segregation hypothesis proposes that CD45 exclusion shifts the local kinase-phosphatase balance to favor TCR phosphorylation. Spatial partitioning may arise from the size difference between the large CD45 extracellular domain and the smaller TCR-pMHC complex, although parsing potential contributions of extracellular protein size, actin activity, and lipid domains is difficult in living cells. Here, we reconstitute segregation of CD45 from bound receptor-ligand pairs using purified proteins on model membranes. Using a model receptor-ligand pair (FRB-FKBP), we first test physical and computational predictions for protein organization at membrane interfaces. We then show that the TCR-pMHC interaction causes partial exclusion of CD45. Comparing two developmentally regulated isoforms of CD45, the larger RABC variant is excluded more rapidly and efficiently (∼50%) than the smaller R0 isoform (∼20%), suggesting that CD45 isotypes could regulate signaling thresholds in different T cell subtypes. Similar to the sensitivity of T cell signaling, TCR-pMHC interactions with Kds of ≤15 µM were needed to exclude CD45. We further show that the coreceptor PD-1 with its ligand PD-L1, immunotherapy targets that inhibit T cell signaling, also exclude CD45. These results demonstrate that the binding energies of physiological receptor-ligand pairs on the T cell are sufficient to create spatial organization at membrane-membrane interfaces.
Keywords: CD45; PD-1; TCR; kinetic segregation; signaling.
Copyright © 2017 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Carbone CB, et al. June 7, 2017. In vitro reconstitution of T cell receptor-mediated segregation of the CD45 phosphatase. bioRxiv, 10.1101/097600.
-
- Brownlie RJ, Zamoyska R. T cell receptor signalling networks: Branched, diversified and bounded. Nat Rev Immunol. 2013;13:257–269. - PubMed
-
- Davis SJ, van der Merwe PA. The kinetic-segregation model: TCR triggering and beyond. Nat Immunol. 2006;7:803–809. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

