Diagonal Earlobe Crease is a Visible Sign for Cerebral Small Vessel Disease and Amyloid-β
- PMID: 29042572
- PMCID: PMC5645376
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-13370-8
Diagonal Earlobe Crease is a Visible Sign for Cerebral Small Vessel Disease and Amyloid-β
Abstract
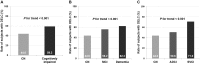
We investigated the frequency and clinical significance of diagonal earlobe crease (DELC) in cognitively impaired patients using imaging biomarkers, such as white matter hyperintensities (WMH) on MRI and amyloid-β (Aβ) PET. A total of 471 cognitively impaired patients and 243 cognitively normal (CN) individuals were included in this study. Compared with CN individuals, cognitively impaired patients had a greater frequency of DELC (OR 1.6, 95% CI 1.1-2.2, P = 0.007). This relationship was more prominent in patients with dementia (OR 1.8, 95% CI 1.2-2.7, P = 0.002) and subcortical vascular cognitive impairment (OR 2.4, 95% CI 1.6-3.6, P < 0.001). Compared with Aβ-negative cognitively impaired patients with minimal WMH, Aβ-positive patients with moderate to severe WMH were significantly more likely to exhibit DELC (OR 7.3, 95% CI 3.4-16.0, P < 0.001). We suggest that DELC can serve as a useful supportive sign, not only for the presence of cognitive impairment, but also for cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) and Aβ-positivity. The relationship between DELC and Aβ-positivity might be explained by the causative role of CSVD in Aβ accumulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Diagonal earlobe crease (Frank's sign) and increased risk of cerebrovascular diseases: review of the literature and implications for clinical practice.Neurol Sci. 2020 Feb;41(2):257-262. doi: 10.1007/s10072-019-04080-2. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Neurol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31641899
-
Brain amyloid β, cerebral small vessel disease, and cognition: A memory clinic study.Neurology. 2020 Nov 24;95(21):e2845-e2853. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000011029. Epub 2020 Oct 12. Neurology. 2020. PMID: 33046617
-
White Matter Hyperintensities Potentiate Hippocampal Volume Reduction in Non-Demented Older Individuals with Abnormal Amyloid-β.J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;55(1):333-342. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160474. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017. PMID: 27662299
-
Amyloid Positivity in the Alzheimer/Subcortical-Vascular Spectrum.Neurology. 2021 Apr 27;96(17):e2201-e2211. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000011833. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Neurology. 2021. PMID: 33722997
-
Novel imaging techniques in cerebral small vessel diseases and vascular cognitive impairment.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 May;1862(5):926-38. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2015.12.010. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26687324 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of White Matter Hyperintensities and Related Risk Factors in Vascular Cognitive Impairment: A Review.Biomolecules. 2021 Jul 27;11(8):1102. doi: 10.3390/biom11081102. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34439769 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of Diagonal Earlobe Crease with Risk of Atrial Fibrillation in Stable Patients with Coronary Artery Disease.J Clin Med. 2024 Sep 23;13(18):5643. doi: 10.3390/jcm13185643. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39337131 Free PMC article.
-
Diagonal earlobe crease (Frank's sign) and increased risk of cerebrovascular diseases: review of the literature and implications for clinical practice.Neurol Sci. 2020 Feb;41(2):257-262. doi: 10.1007/s10072-019-04080-2. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Neurol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31641899
-
Advancements in Frank's sign Identification using deep learning on 3D brain MRI.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 18;15(1):2383. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82756-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39827273 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Frank ST. Aural sign of coronary-artery disease. N Engl J Med. 1973;289:327–328. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

