Theranostics in nuclear medicine practice
- PMID: 29042793
- PMCID: PMC5633297
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S140671
Theranostics in nuclear medicine practice
Abstract
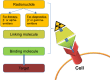
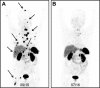
The importance of personalized medicine has been growing, mainly due to a more urgent need to avoid unnecessary and expensive treatments. In nuclear medicine, the theranostic approach is an established tool for specific molecular targeting, both for diagnostics and therapy. The visualization of potential targets can help predict if a patient will benefit from a particular treatment. Thanks to the quick development of radiopharmaceuticals and diagnostic techniques, the use of theranostic agents has been continually increasing. In this article, important milestones of nuclear therapies and diagnostics in the context of theranostics are highlighted. It begins with a well-known radioiodine therapy in patients with thyroid cancer and then progresses through various approaches for the treatment of advanced cancer with targeted therapies. The aim of this review was to provide a summary of background knowledge and current applications, and to identify the advantages of targeted therapies and imaging in nuclear medicine practices.
Keywords: PET/CT; diagnostics; nuclear medicine; personalized medicine; theranostics; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Gridelli C. Does chemotherapy have a role as palliative therapy for unfit or elderly patients with non-small-cell lung cancer? Lung Cancer. 2002;38(Suppl 2):S45–S50. - PubMed
-
- Richardson JL, Marks G, Levine A. The influence of symptoms of disease and side effects of treatment on compliance with cancer therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1988;6(11):1746–1752. - PubMed
-
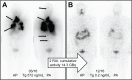
- Gerard SK, Cavalieri RR. I-123 diagnostic thyroid tumor whole-body scanning with imaging at 6, 24, and 48 hours. Clin Nucl Med. 2002;27(1):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Alzahrani AS, AlShaikh O, Tuli M, Al-Sugair A, Alamawi R, Al-Rasheed MM. Diagnostic value of recombinant human thyrotropin-stimulated 123I whole-body scintigraphy in the follow-up of patients with differentiated thyroid cancer. Clin Nucl Med. 2012;37(3):229–234. - PubMed
-
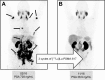
- Walrand S, Hesse M, Renaud L, Jamar F. The impact of image reconstruction bias on PET/CT 90Y dosimetry after radioembolization. J Nucl Med. 2015;56(3):494–495. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

