Crizotinib, a MET inhibitor, inhibits growth, migration, and invasion of breast cancer cells in vitro and synergizes with chemotherapeutic agents
- PMID: 29042798
- PMCID: PMC5634371
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S148604
Crizotinib, a MET inhibitor, inhibits growth, migration, and invasion of breast cancer cells in vitro and synergizes with chemotherapeutic agents
Abstract
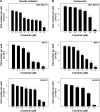
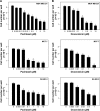
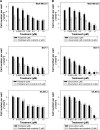
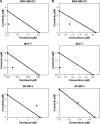
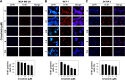
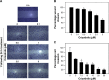
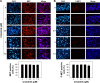
MET is a receptor tyrosine kinase known for its pleiotropic effects in tumorigenesis. Dysregulations of MET expression and/or signaling have been reported and determined to be associated with inferior outcomes in breast cancer patients rendering MET a versatile candidate for targeted therapeutic intervention. Crizotinib is a multi-targeted small-molecule kinase inhibitor for MET, ALK, and ROS1 kinases. This study evaluated the anti-proliferative, cytotoxic, anti-migratory, and anti-invasive effects of crizotinib in breast cancer cells in vitro. Cell viability was assessed by 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) colorimetric assay. In vitro wound-healing assay was used to examine the effect of crizotinib on breast cancer cell migration. The expressions of Ki-67, MET, and phospho-MET receptors were characterized using immunofluorescence staining. Results showed that crizotinib has significant anti-proliferative activity on all mammary tumor cells with IC50 values of 5.16, 1.5, and 3.85 µM in MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, and SK-BR-3 cells, respectively. Crizotinib induced cytotoxic effects in all breast cancer cells examined. Combined treatment of small dose of crizotinib with paclitaxel or doxorubicin exhibited a highly synergistic inhibition of growth of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells with combination index values <1 while no significant effect was observed in SK-BR-3 cells compared with individual compounds. Treatment with crizotinib demonstrated a remarkable reduction in the expression of Ki-67 protein in all 3 tested cell lines. Crizotinib inhibited migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells in a dose-dependent fashion. Crizotinib reduced MET receptor activation in MDA-MB-231 cells when treated at effective concentrations. In conclusion, crizotinib suppressed proliferation, migration, and invasion of breast cancer cells in vitro. The results of this study demonstrated that combined treatment of crizotinib with chemotherapeutic agents resulted in a synergistic growth inhibition of specific breast cancer cell lines.
Keywords: MET receptor; breast cancer; chemotherapy; crizotinib; invasion; migration.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Crizotinib induced antitumor activity and synergized with chemotherapy and hormonal drugs in breast cancer cells via downregulating MET and estrogen receptor levels.Invest New Drugs. 2021 Feb;39(1):77-88. doi: 10.1007/s10637-020-00989-0. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Invest New Drugs. 2021. PMID: 32833135
-
Combined crizotinib and endocrine drugs inhibit proliferation, migration, and colony formation of breast cancer cells via downregulation of MET and estrogen receptor.Med Oncol. 2021 Jan 15;38(1):8. doi: 10.1007/s12032-021-01458-1. Med Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33449292
-
[Effect and mechanism of silibinin on the inhibition of ALK positive NSCLC cells by sensitizing crizotinib].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2017 Sep 23;39(9):650-656. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-3766.2017.09.003. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28926892 Chinese.
-
Crizotinib, a small-molecule dual inhibitor of the c-Met and ALK receptor tyrosine kinases.Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2010 Dec;11(12):1477-90. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2010. PMID: 21154129 Review.
-
Targeted therapies in non-small cell lung cancer: a focus on ALK/ROS1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2018 Jan;18(1):71-80. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2018.1412260. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2018. PMID: 29187012 Review.
Cited by
-
Crizotinib induced antitumor activity and synergized with chemotherapy and hormonal drugs in breast cancer cells via downregulating MET and estrogen receptor levels.Invest New Drugs. 2021 Feb;39(1):77-88. doi: 10.1007/s10637-020-00989-0. Epub 2020 Aug 24. Invest New Drugs. 2021. PMID: 32833135
-
MERTK in cancer therapy: Targeting the receptor tyrosine kinase in tumor cells and the immune system.Pharmacol Ther. 2020 Sep;213:107577. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107577. Epub 2020 May 14. Pharmacol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32417270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular mechanism(s) of regulation(s) of c-MET/HGF signaling in head and neck cancer.Mol Cancer. 2022 Jan 26;21(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01503-1. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35081970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Higher cMET dependence of sacral compared to clival chordoma cells: contributing to a better understanding of cMET in chordoma.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 14;11(1):12466. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-92018-0. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34127734 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic Analysis, Antiproliferative, Anti-Migratory, and Anti-Invasive Potential of Amlodipine in Lung Cancer Cells.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 Feb 19;19:1215-1229. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S484561. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 39991087 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406(6797):747–752. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

